BluesLegend
Diamond Member
Suck on the 2nd amendment you lame ass liberals.
Follow along with the video below to see how to install our site as a web app on your home screen.
Note: This feature may not be available in some browsers.
Unlock unbeatable offers today. Shop here: https://amzn.to/4cEkqYs 🎁
A lot of things can be bi-directional. Studies suggest this for this reason. You have no good reason to actually believe that shit. Your confidence is based on nothing. Either way, nothing good comes from more higher gun ownership. Clearly people owning more guns doesn’t stop the crime rate anyway. The result is more bad people with guns.No, it isn't as the article clearly states and I have shown. Increased gun ownership is far more likely to be a result of violent crime than the cause. I doubt you even bothered to read what you linked to and have no idea what it says. That's why I quoted it. But apparently you didn't bother to read that either.It’s linked in the article idiot.SHOW ME THE FUCKING RESEARCH OR FUCK OFF, YAHOO "NEWS"!!!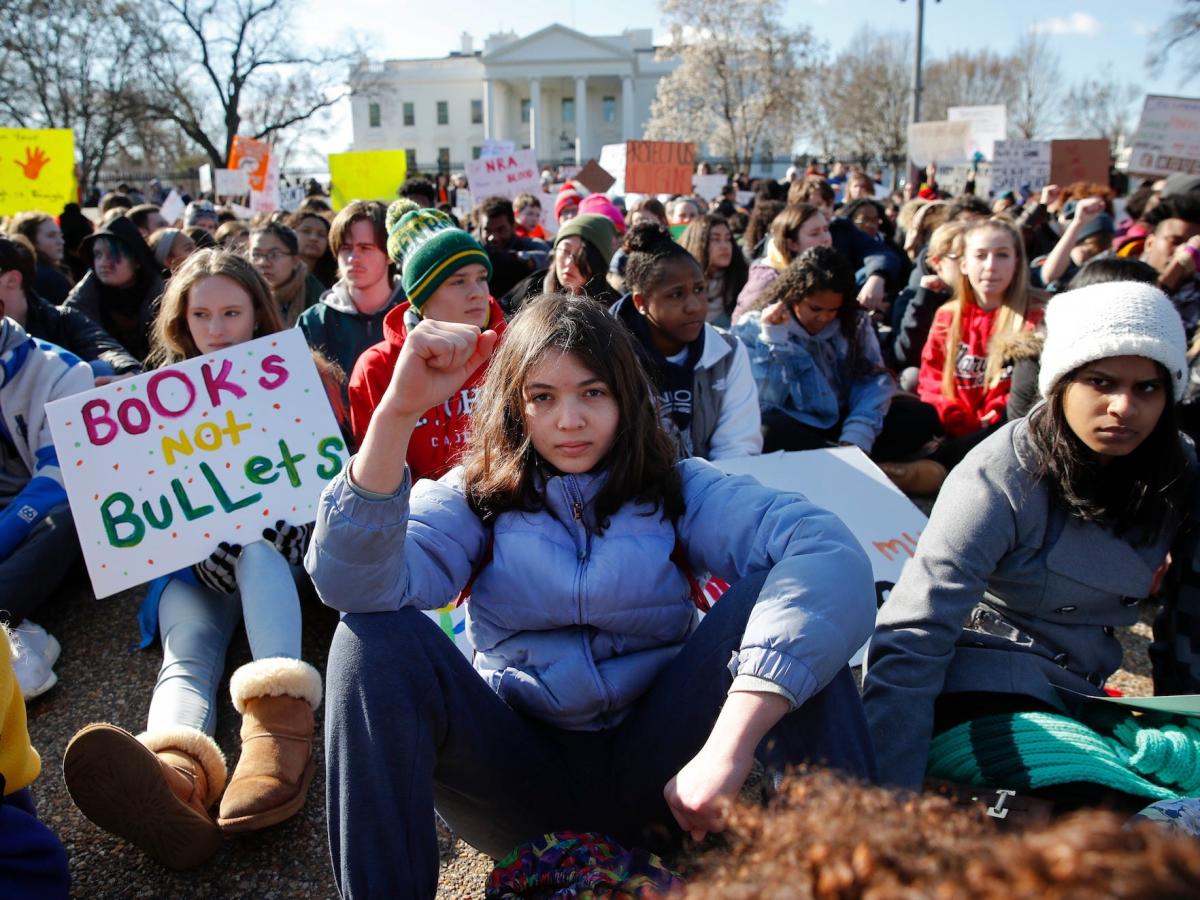
New research puts the 'good guy with a gun' idea to rest: Loose concealed-carry laws are linked to more firearm homicides
States with looser concealed-carry laws have higher rates of gun homicide. And higher gun-ownership rates are associated with more mass shootings.www.yahoo.com
A new study found that states with looser concealed-carry gun laws have higher rates of gun homicide.
The results also showed that higher levels of gun ownership are associated with more mass shootings.
The study suggests the US could reduce gun violence by lowering levels of gun ownership and passing stricter concealed-carry laws.
Visit Business Insider's homepage for more stories.
The "good guy with a gun" theory goes like this: If more well-intentioned people carry guns, there's a higher chance of stopping a violent shooter.
Unfortunately, that's not how it works in real life, according to new research published in the journal Justice Quarterly. The study found that laws allowing more people to carry guns in public are associated with a rise in gun violence. The results also showed that the higher a state's gun-ownership rate, the more likely a mass shooting is.
Right-to-Carry Concealed Weapon Laws and Homicide in Large U.S. Counties: The Effect on Weapon Types, Victim Characteristics, and Victim-Offender Relationships By DAVID E. OLSON AND MICHAEL D. MALTZ, Journal of Law and Economics, October 2001
Our results indicated that the direction of effect of the shall-issue law on total SHR homicide rates was similar to that obtained by Lott and Mustard, although the magnitude of the effect was somewhat smaller and was statistically significant at the 7 percent level. In our analysis, which included only counties with a 1977 population of 100,000 or more, laws allowing for concealed weapons were associated with a 6.52 percent reduction in total homicides (Table 2). By comparison, Lott and Mustard found the concealed weapon dummy variable to be associated with a 7.65 percent reduction in total homicides across all counties and a 9 percent reduction in homicides when only large counties (populations of 100,000 or more) were included.43
====
====
http://johnrlott.tripod.com/Plassmann_Whitley.pdf
COMMENTS
Confirming ìMore Guns, Less Crimeî Florenz Plassmann* & John Whitley**
CONCLUSION Analyzing county-level data for the entire United States from 1977 to 2000, we find annual reductions in murder rates between 1.5% and 2.3% for each additional year that a right-to-carry law is in effect.
For the first five years that such a law is in effect, the total benefit from reduced crimes usually ranges between about $2 and $3 billion per year.
The results are very similar to earlier estimates using county-level data from 1977 to 1996. We appreciate the continuing effort that Ayres and Donohue have made in discussing the impact of right-to-carry laws on crime rates. Yet we believe that both the new evidence provided by them as well as our new results show consistently that right-to-carry laws reduce crime and save lives. Unfortunately, a few simple mistakes lead Ayres and Donohue to incorrectly claim that crime rates significantly increase after right-to-carry laws are initially adopted and to misinterpret the significance of their own estimates that examined the year-to-year impact of the law.
http://crimeresearch.org/wp-content...An-Exercise-in-Replication.proof_.revised.pdf
~ The Impact of Right-to-Carry Laws on Crime: An Exercise in Replication1
Carlisle E. Moody College of William and Mary - Department of Economics, Virginia 23187, U.S.A. E-mail: [email protected] Thomas B. Marvell Justec Research, Virginia 23185, U.S.A. Paul R. Zimmerman U.S. Federal Trade Commission - Bureau of Economics, Washington, D.C., U.S.A. Fasil Alemante College of William and Mary, Virginia 23187, U.S.A.
Abstract: In an article published in 2011, Aneja, Donohue and Zhang found that shall-issue or right-to-carry (RTC) concealed weapons laws have no effect on any crime except for a positive effect on assault.
This paper reports a replication of their basic findings and some corresponding robustness checks, which reveal a serious omitted variable problem.
Once corrected for omitted variables, the most robust result, confirmed using both county and state data, is that RTC laws significantly reduce murder.
====
===An examination of the effects of concealed weapons laws and assault weapons bans on state-level murder rates
Mark Gius
Abstract
The purpose of the present study is to determine the effects of state-level assault weapons bans and concealed weapons laws on state-level murder rates.
Using data for the period 1980 to 2009 and controlling for state and year fixed effects, the results of the present study suggest that states with restrictions on the carrying of concealed weapons had higher gun-related murder rates than other states.
It was also found that assault weapons bans did not significantly affect murder rates at the state level. These results suggest that restrictive concealed weapons laws may cause an increase in gun-related murders at the state level. The results of this study are consistent with some prior research in this area, most notably Lott and Mustard (1997).
“The Debate on Shall-Issue Laws” by Carlisle e. Moody and Thomas B. Marvell, published in Econ Journal Watch, volume 5, number 3, September 2008 It is also available here..
Summary and Conclusion
Many articles have been published finding that shall-issue laws reduce crime. Only one article, by Ayres and Donohue who employ a model that combines a dummy variable with a post-law trend, claims to find that shall-issue laws increase crime.
However, the only way that they can produce the result that shall-issue laws increase crime is to confine the span of analysis to five years
. We show, using their own estimates, that if they had extended their analysis by one more year, they would have concluded that these laws reduce crime.
Since most states with shallissue laws have had these laws on the books for more than five years, and the law will presumably remain on the books for some time, the only relevant analysis extends beyond five years. We extend their analysis by adding three more years of data, control for the effects of crack cocaine, control for dynamic effects, and correct the standard errors for clustering.
We find that there is an initial increase in crime due to passage of the shall-issue law that is dwarfed over time by the decrease in crime associated with the post-law trend.
These results are very similar to those of Ayres and Donohue, properly interpreted.
The modified Ayres and Donohue model finds that shall-issue laws significantly reduce murder and burglary across all the adopting states. These laws appear to significantly increase assault, and have no net effect on rape, robbery, larceny, or auto theft. However, in the long run only the trend coefficients matter. We estimate a net benefit of $450 million per year as a result of the passage of these laws. We also estimate that, up through 2000, there was a cumulative overall net benefit of these laws of $28 billion since their passage. We think that there is credible statistical evidence that these laws lower the costs of crime. But at the very least, the present study should neutralize any “more guns, more crime” thinking based on Ayres and Donohue’s work in the Stanford Law Review
Okay the crime rate in general has deceased. You making this a correlation about gun ownership is based on nothing. There is no direct connection between the two. You’re just pretending there is.A lot of things can be bi-directional. Studies suggest this for this reason. You have no good reason to actually believe that shit. Your confidence is based on nothing. Either way, nothing good comes from more higher gun ownership. Clearly people owning more guns doesn’t stop the crime rate anyway. The result is more bad people with guns.No, it isn't as the article clearly states and I have shown. Increased gun ownership is far more likely to be a result of violent crime than the cause. I doubt you even bothered to read what you linked to and have no idea what it says. That's why I quoted it. But apparently you didn't bother to read that either.It’s linked in the article idiot.SHOW ME THE FUCKING RESEARCH OR FUCK OFF, YAHOO "NEWS"!!!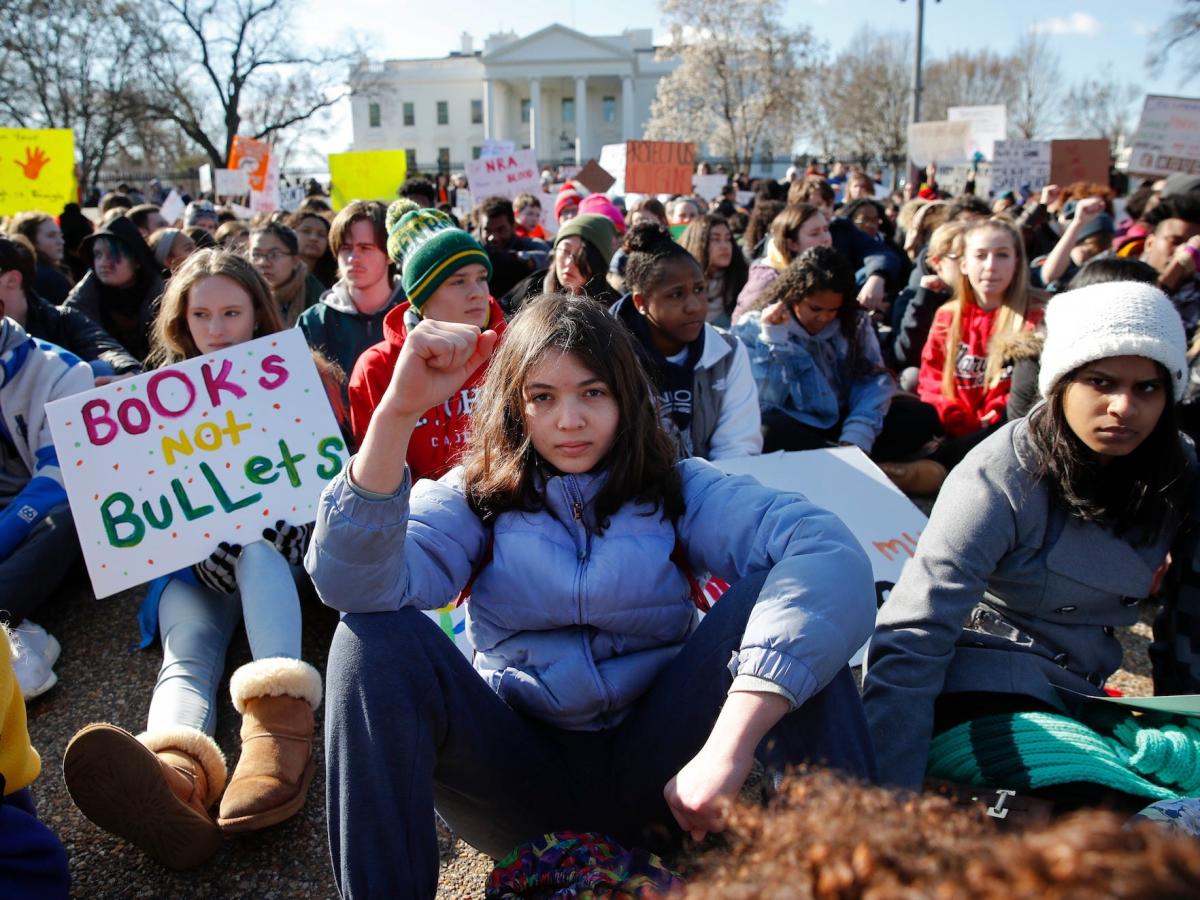
New research puts the 'good guy with a gun' idea to rest: Loose concealed-carry laws are linked to more firearm homicides
States with looser concealed-carry laws have higher rates of gun homicide. And higher gun-ownership rates are associated with more mass shootings.www.yahoo.com
A new study found that states with looser concealed-carry gun laws have higher rates of gun homicide.
The results also showed that higher levels of gun ownership are associated with more mass shootings.
The study suggests the US could reduce gun violence by lowering levels of gun ownership and passing stricter concealed-carry laws.
Visit Business Insider's homepage for more stories.
The "good guy with a gun" theory goes like this: If more well-intentioned people carry guns, there's a higher chance of stopping a violent shooter.
Unfortunately, that's not how it works in real life, according to new research published in the journal Justice Quarterly. The study found that laws allowing more people to carry guns in public are associated with a rise in gun violence. The results also showed that the higher a state's gun-ownership rate, the more likely a mass shooting is.
You are an idiot....27 years of actual increased gun ownership shows.....that normal people who own and carry guns does not increase the gun crime rate....at all....
Over the last 27 years, we went from 200 million guns in private hands in the 1990s and 4.7 million people carrying guns for self defense in 1997...to close to 400-600 million guns in private hands and over 18.6 million people carrying guns for self defense in 2018...guess what happened...
-- gun murder down 49%
--gun crime down 75%
--violent crime down 72%
Gun Homicide Rate Down 49% Since 1993 Peak; Public Unaware
Compared with 1993, the peak of U.S. gun homicides, the firearm homicide rate was 49% lower in 2010, and there were fewer deaths, even though the nation’s population grew. The victimization rate for other violent crimes with a firearm—assaults, robberies and sex crimes—was 75% lower in 2011 than in 1993. Violent non-fatal crime victimization overall (with or without a firearm) also is down markedly (72%) over two decades.
----
Maine tops ‘safest states’ rankings four years after removing major gun restriction
When Maine passed a “Constitutional Carry” law allowing Maine residents to carry a concealed firearm without any special permit in 2015, opponents of the law forecast a dangerous future for the state. They said the new law would hurt public safety and put Maine kids at risk.
One state representative who opposed the bill went so far as to say it would give Mainers a reason to be afraid every time they went out in public or to work.
Another state representative suggested the law would lead to violent criminals with recent arrests and convictions legally carrying handguns.
-----
Now four years later, Maine has been named the safest state in the nation according to US News and World Report’s public safety rankings, which measures the fifty states based on crime data.
Ranking as the top safest state for violent crime and fourth for property crime, Maine edges out another New England state, Vermont, for the top spot. Of note, Vermont also is a “Constitutional Carry” state. New Hampshire ranks third in the national rankings, giving New England all three of the top spots in the nation.
In 2018, Maine was edged out by Vermont in the same “safest states” ranking, but declared the best state overall in the broader “Crime and Corrections” category.
In 2017, using a different methodology, Maine was ranked second among the fifty states in the “Crime and Corrections” category and also second in the categories used to rank the “safest states.”
The U.S. News and World Report “Best States” rankings are built in partnership with McKinsey & Company, a firm that works closely with state leaders around the nation.
Maine has also ranked at the top of other state rankings. WalletHub.com recently ranked Maine second in “Personal and Residential Safety” among the fifty states, and third overall.
=============
Bolsonaro's Brazil, More Legal Guns, Homicide Rates Down Precipitously
In December, 2018, in an article published by the Wall Street Journal, this pronouncement was made. From the wsj.com:
Homicides in Brazil were at historic highs in 2017. They dropped a bit in 2018, as candidate Bolsonaro ran on reform of the gun laws to allow self defense, and reform of the law to get tough on crime. The homicide numbers dropped from 59,000 in 2017, to 51,000 in 2018. President Bolsonaro was elected in October of 2018.Now, Brazil is set to embark on an experiment that will determine what happens when you loosen gun restrictions in a country battling an overpowering wave of gun crime.
After taking office on 1 January, 2019, President Bolsonaro issued his first decree reforming some of Brazil's extreme gun laws on 15 January, 2019. The drop in Brazil's homicide rate accelerated.
-------
Early in the Bolsonaro presidency, a Brazilian lawyer prediceted the homicide rate would drop. From ammoland.com:
The rate reduction was not quite that high. Only 10,000 lives were saved. From wtop.com:César Mello, asked that I include information that early reports are showing a 25% drop in Brazil's homicide rate, in the first quarter of 2019. If this trend continues, 16,000 lives will have been saved in the first year of President Bolsonaro's time in office.
When translated to homicide rates, the rate dropped 17% in 2018, then 23% more in 2019. The population of Brazil in 2019 was 210 million. The rate of homicides per 100,000 was 19.83. That is less than 2/3 of the homicide rate in 2017, which was 30.8.Brazil had 41,635 killings in 2019, down 19% from the prior year and the least number of homicides since 2007, when the so-called Violence Monitor index was launched. It is a partnership between the non-profit Brazilian Forum of Public Security, the University of Sao Paulo’s Center for the Study of Violence, and news website G1, which published the data Friday.
Lol this study is cherry picking instances where a good guy with a gun happened - a grand total of 25 times lol. Why this doesn’t matter is because the large majority of mass shootings did NOT have a good guy with a gun.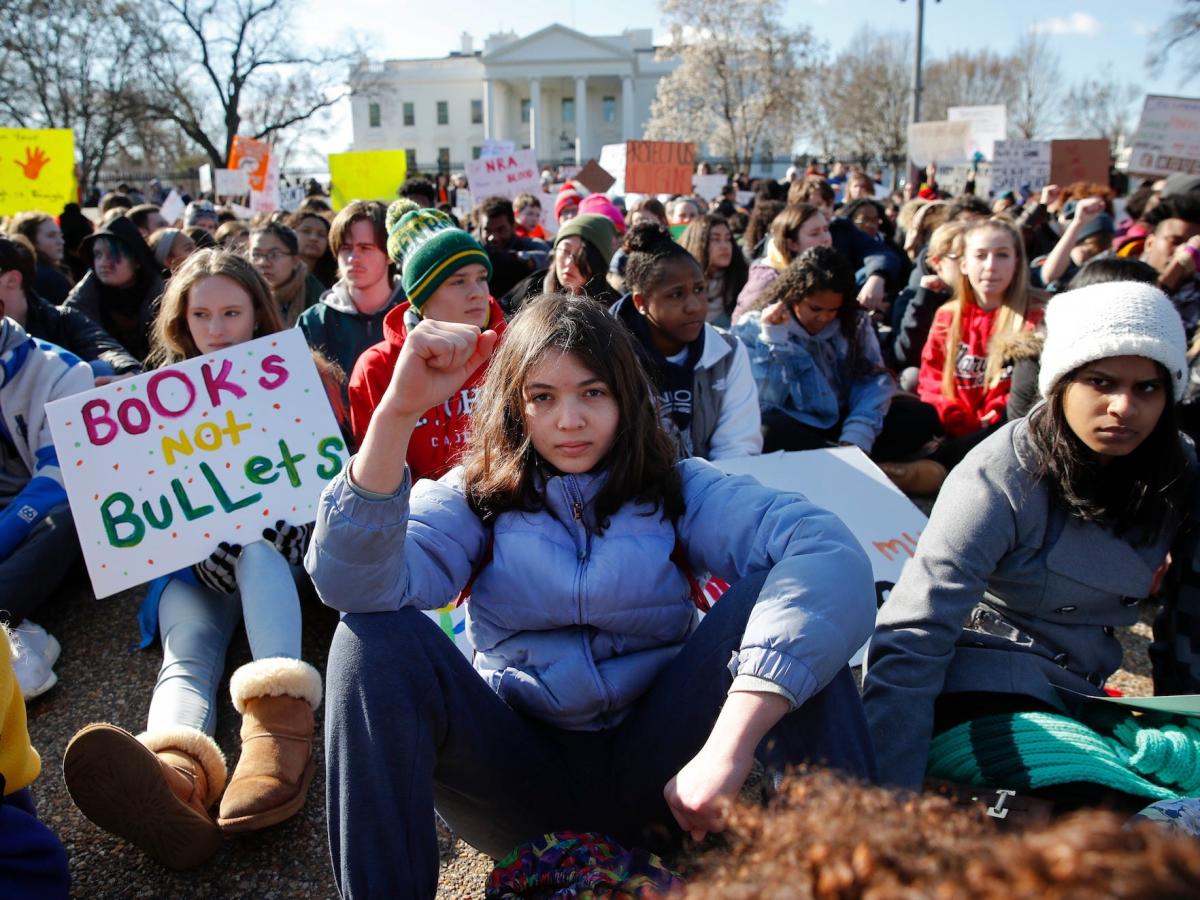
New research puts the 'good guy with a gun' idea to rest: Loose concealed-carry laws are linked to more firearm homicides
States with looser concealed-carry laws have higher rates of gun homicide. And higher gun-ownership rates are associated with more mass shootings.www.yahoo.com
A new study found that states with looser concealed-carry gun laws have higher rates of gun homicide.
The results also showed that higher levels of gun ownership are associated with more mass shootings.
The study suggests the US could reduce gun violence by lowering levels of gun ownership and passing stricter concealed-carry laws.
Visit Business Insider's homepage for more stories.
The "good guy with a gun" theory goes like this: If more well-intentioned people carry guns, there's a higher chance of stopping a violent shooter.
Unfortunately, that's not how it works in real life, according to new research published in the journal Justice Quarterly. The study found that laws allowing more people to carry guns in public are associated with a rise in gun violence. The results also showed that the higher a state's gun-ownership rate, the more likely a mass shooting is.
Here...some actual truth....
Armed Citizens Are Successful 94% Of The Time At Active Shooter Events [FBI]
Of all the active shooter events there were 33 at which an armed citizen was present. Of those, Armed Citizens were successful at stopping the Active shooter 75.8% of the time (25 incidents) and were successful in reducing the loss of life in an additional 18.2% (6) of incidents. In only 2 of the 33 incidents (6.1%) was the Armed Citizen(s) not helpful in any way in stopping the active shooter or reducing the loss of life.
Thus the headline of our report that Armed Citizens Are Successful 94% Of The Time At Active Shooter Events.
In the 2 incidents at which the armed citizen “failed” to stop or slow the active shooter, one is the previously mentioned incident with hunters. The other is an incident in which the CCWer was shot in the back in a Las Vegas Walmart when he failed to identify that there were 2 Active Shooters involved in the attack. He neglected to identify the one that shot him in the back while he was trying to ambush the other perpetrator.
We also decided to look at the breakdown of events that took place in gun free zones and the relative death toll from events in gun free zones vs non-gun-free zones.
Of the 283 incidents in our data pool, we were unable to identify if the event took place in a gun-free zone in a large number (41%) of the events. Most of the events took place at a business, church, home, or other places at which as a rule of law it is not a gun free zone but potentially could have been declared one by the property owner. Without any information in the FBI study or any indication one way or the other from the news reports, we have indicated that event with a question mark.
If you look at all of the Active Shooter events (pie chart on the top) you see that for those which we have the information, almost twice as many took place in gun free zones than not; but realistically the vast majority of those for which we have no information (indicated as ?) are probably NOT gun free zones.
If you isolate just the events at which 8 or more people were killed the data paints a different picture (pie chart on the bottom). In these incidents, 77.8% took place in a gun-free zone suggesting that gun free zones lead to a higher death rate vs active shooter events in general
=====
One of the final metrics we thought was important to consider is the potential tendency for armed citizens to injure or kill innocent people in their attempt to “save the day.” A common point in political discussions is to point out the lack of training of most armed citizens and the decrease in safety inherent in their presence during violent encounters.
As you can see below, however, at the 33 incidents at which Armed Citizens were present, there were zero situations at which the Armed Citizen injured or killed an innocent person. It never happened.
Then start by disarming Democrats and passing laws making it more difficult for them to have gun ownership.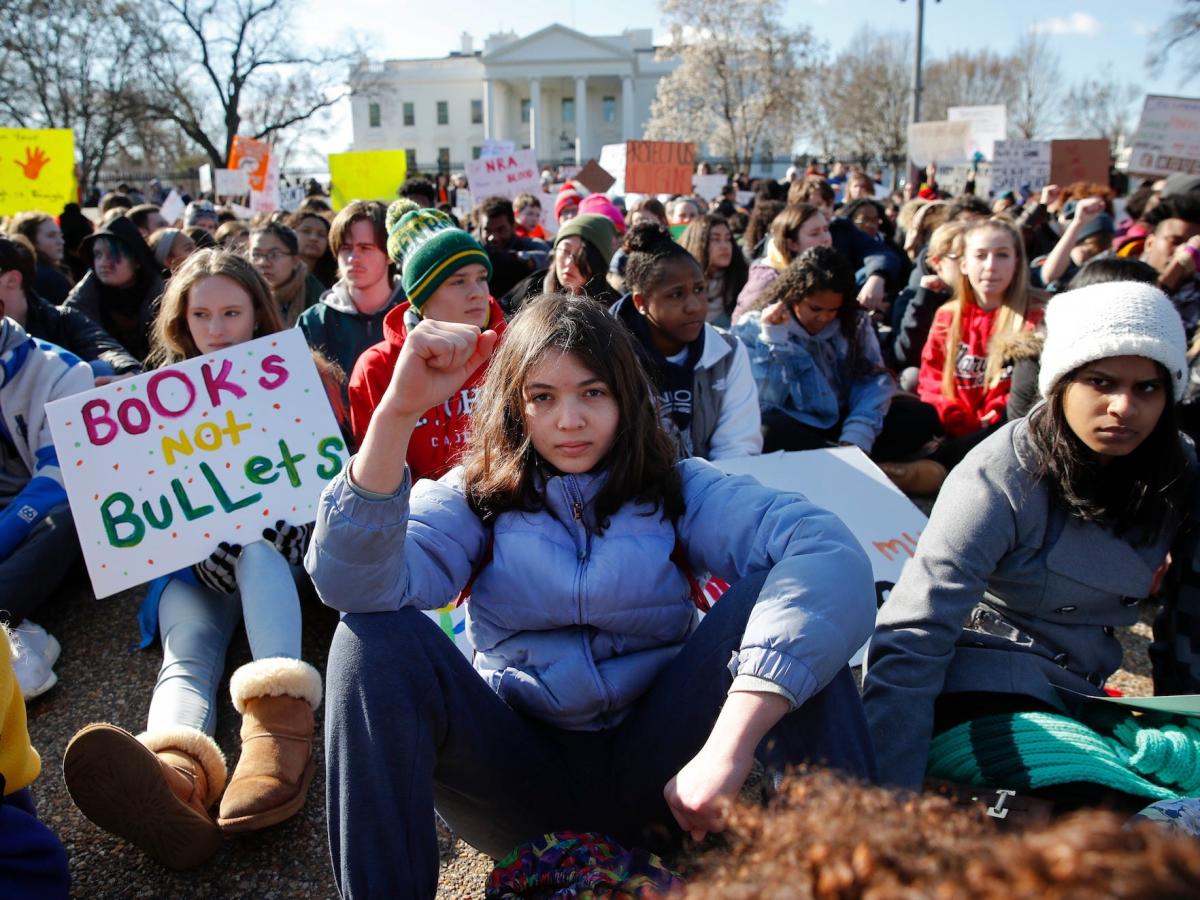
New research puts the 'good guy with a gun' idea to rest: Loose concealed-carry laws are linked to more firearm homicides
States with looser concealed-carry laws have higher rates of gun homicide. And higher gun-ownership rates are associated with more mass shootings.www.yahoo.com
A new study found that states with looser concealed-carry gun laws have higher rates of gun homicide.
The results also showed that higher levels of gun ownership are associated with more mass shootings.
The study suggests the US could reduce gun violence by lowering levels of gun ownership and passing stricter concealed-carry laws.
Visit Business Insider's homepage for more stories.
The "good guy with a gun" theory goes like this: If more well-intentioned people carry guns, there's a higher chance of stopping a violent shooter.
Unfortunately, that's not how it works in real life, according to new research published in the journal Justice Quarterly. The study found that laws allowing more people to carry guns in public are associated with a rise in gun violence. The results also showed that the higher a state's gun-ownership rate, the more likely a mass shooting is.
Okay again , the violent crime rates across the board have been going down. My study specifically makes the connection between gun ownership and GUN DEATHS SPECIFICALLY. Your so called studies are simply looking at crime trends that have already been going down anyway.A lot of things can be bi-directional. Studies suggest this for this reason. You have no good reason to actually believe that shit. Your confidence is based on nothing. Either way, nothing good comes from more higher gun ownership. Clearly people owning more guns doesn’t stop the crime rate anyway. The result is more bad people with guns.No, it isn't as the article clearly states and I have shown. Increased gun ownership is far more likely to be a result of violent crime than the cause. I doubt you even bothered to read what you linked to and have no idea what it says. That's why I quoted it. But apparently you didn't bother to read that either.It’s linked in the article idiot.SHOW ME THE FUCKING RESEARCH OR FUCK OFF, YAHOO "NEWS"!!!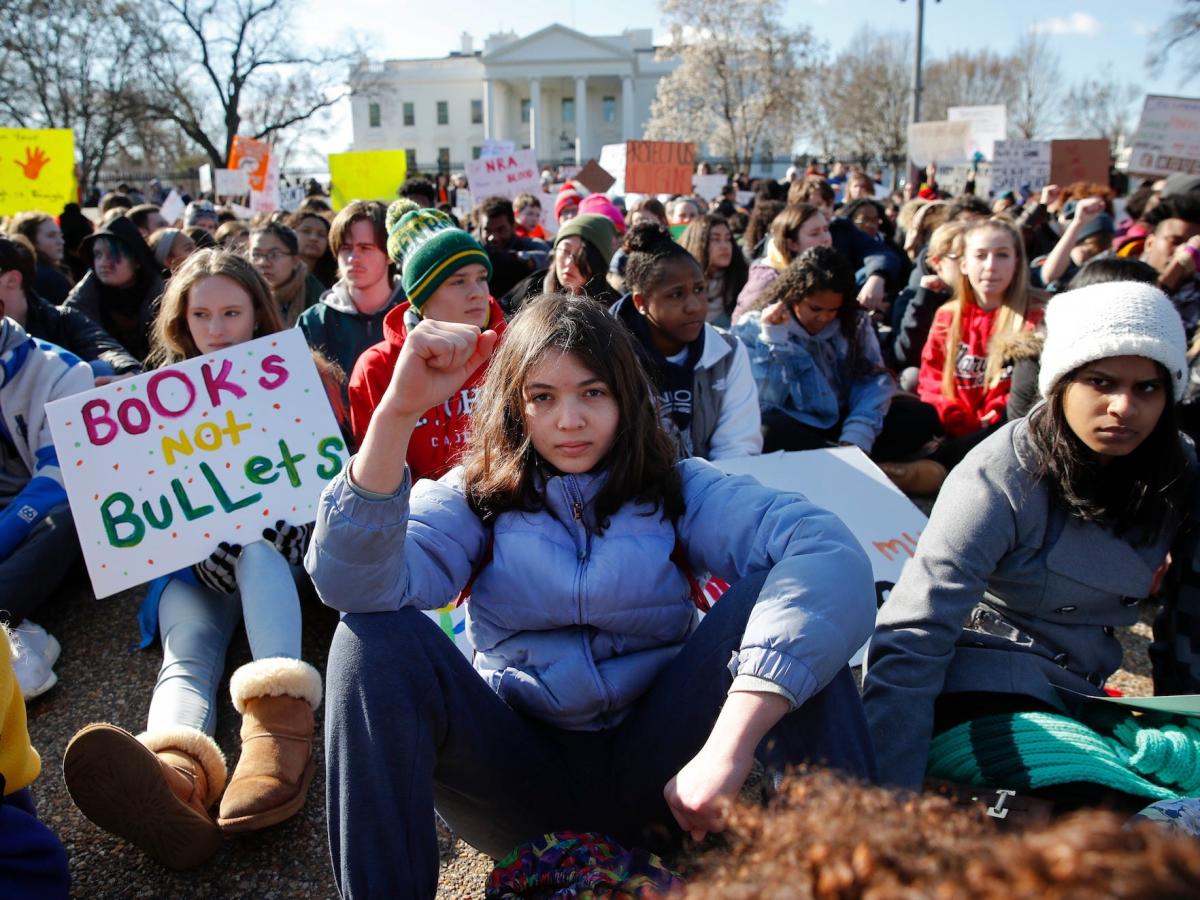
New research puts the 'good guy with a gun' idea to rest: Loose concealed-carry laws are linked to more firearm homicides
States with looser concealed-carry laws have higher rates of gun homicide. And higher gun-ownership rates are associated with more mass shootings.www.yahoo.com
A new study found that states with looser concealed-carry gun laws have higher rates of gun homicide.
The results also showed that higher levels of gun ownership are associated with more mass shootings.
The study suggests the US could reduce gun violence by lowering levels of gun ownership and passing stricter concealed-carry laws.
Visit Business Insider's homepage for more stories.
The "good guy with a gun" theory goes like this: If more well-intentioned people carry guns, there's a higher chance of stopping a violent shooter.
Unfortunately, that's not how it works in real life, according to new research published in the journal Justice Quarterly. The study found that laws allowing more people to carry guns in public are associated with a rise in gun violence. The results also showed that the higher a state's gun-ownership rate, the more likely a mass shooting is.
Here...actual research proving you wrong...
Right-to-Carry Concealed Weapon Laws and Homicide in Large U.S. Counties: The Effect on Weapon Types, Victim Characteristics, and Victim-Offender Relationships By DAVID E. OLSON AND MICHAEL D. MALTZ, Journal of Law and Economics, October 2001
Our results indicated that the direction of effect of the shall-issue law on total SHR homicide rates was similar to that obtained by Lott and Mustard, although the magnitude of the effect was somewhat smaller and was statistically significant at the 7 percent level. In our analysis, which included only counties with a 1977 population of 100,000 or more, laws allowing for concealed weapons were associated with a 6.52 percent reduction in total homicides (Table 2). By comparison, Lott and Mustard found the concealed weapon dummy variable to be associated with a 7.65 percent reduction in total homicides across all counties and a 9 percent reduction in homicides when only large counties (populations of 100,000 or more) were included.43
====
====
http://johnrlott.tripod.com/Plassmann_Whitley.pdf
COMMENTS
Confirming ìMore Guns, Less Crimeî Florenz Plassmann* & John Whitley**
CONCLUSION Analyzing county-level data for the entire United States from 1977 to 2000, we find annual reductions in murder rates between 1.5% and 2.3% for each additional year that a right-to-carry law is in effect.
For the first five years that such a law is in effect, the total benefit from reduced crimes usually ranges between about $2 and $3 billion per year.
The results are very similar to earlier estimates using county-level data from 1977 to 1996. We appreciate the continuing effort that Ayres and Donohue have made in discussing the impact of right-to-carry laws on crime rates. Yet we believe that both the new evidence provided by them as well as our new results show consistently that right-to-carry laws reduce crime and save lives. Unfortunately, a few simple mistakes lead Ayres and Donohue to incorrectly claim that crime rates significantly increase after right-to-carry laws are initially adopted and to misinterpret the significance of their own estimates that examined the year-to-year impact of the law.
http://crimeresearch.org/wp-content...An-Exercise-in-Replication.proof_.revised.pdf
~ The Impact of Right-to-Carry Laws on Crime: An Exercise in Replication1
Carlisle E. Moody College of William and Mary - Department of Economics, Virginia 23187, U.S.A. E-mail: [email protected] Thomas B. Marvell Justec Research, Virginia 23185, U.S.A. Paul R. Zimmerman U.S. Federal Trade Commission - Bureau of Economics, Washington, D.C., U.S.A. Fasil Alemante College of William and Mary, Virginia 23187, U.S.A.
Abstract: In an article published in 2011, Aneja, Donohue and Zhang found that shall-issue or right-to-carry (RTC) concealed weapons laws have no effect on any crime except for a positive effect on assault.
This paper reports a replication of their basic findings and some corresponding robustness checks, which reveal a serious omitted variable problem.
Once corrected for omitted variables, the most robust result, confirmed using both county and state data, is that RTC laws significantly reduce murder.
====
===An examination of the effects of concealed weapons laws and assault weapons bans on state-level murder rates
Mark Gius
Abstract
The purpose of the present study is to determine the effects of state-level assault weapons bans and concealed weapons laws on state-level murder rates.
Using data for the period 1980 to 2009 and controlling for state and year fixed effects, the results of the present study suggest that states with restrictions on the carrying of concealed weapons had higher gun-related murder rates than other states.
It was also found that assault weapons bans did not significantly affect murder rates at the state level. These results suggest that restrictive concealed weapons laws may cause an increase in gun-related murders at the state level. The results of this study are consistent with some prior research in this area, most notably Lott and Mustard (1997).
“The Debate on Shall-Issue Laws” by Carlisle e. Moody and Thomas B. Marvell, published in Econ Journal Watch, volume 5, number 3, September 2008 It is also available here..
Summary and Conclusion
Many articles have been published finding that shall-issue laws reduce crime. Only one article, by Ayres and Donohue who employ a model that combines a dummy variable with a post-law trend, claims to find that shall-issue laws increase crime.
However, the only way that they can produce the result that shall-issue laws increase crime is to confine the span of analysis to five years
. We show, using their own estimates, that if they had extended their analysis by one more year, they would have concluded that these laws reduce crime.
Since most states with shallissue laws have had these laws on the books for more than five years, and the law will presumably remain on the books for some time, the only relevant analysis extends beyond five years. We extend their analysis by adding three more years of data, control for the effects of crack cocaine, control for dynamic effects, and correct the standard errors for clustering.
We find that there is an initial increase in crime due to passage of the shall-issue law that is dwarfed over time by the decrease in crime associated with the post-law trend.
These results are very similar to those of Ayres and Donohue, properly interpreted.
The modified Ayres and Donohue model finds that shall-issue laws significantly reduce murder and burglary across all the adopting states. These laws appear to significantly increase assault, and have no net effect on rape, robbery, larceny, or auto theft. However, in the long run only the trend coefficients matter. We estimate a net benefit of $450 million per year as a result of the passage of these laws. We also estimate that, up through 2000, there was a cumulative overall net benefit of these laws of $28 billion since their passage. We think that there is credible statistical evidence that these laws lower the costs of crime. But at the very least, the present study should neutralize any “more guns, more crime” thinking based on Ayres and Donohue’s work in the Stanford Law Review
Taking apart ayre and donahue one....
“The Debate on Shall-Issue Laws” by Carlisle e. Moody and Thomas B. Marvell, published in Econ Journal Watch, volume 5, number 3, September 2008 It is also available here..
Abstract
“Shall-issue” laws require authorities to issue concealed-weapons permits to anyone who applies, unless the applicant has a criminal record or a history of mental illness. A large number of studies indicate that shall-issue laws reduce crime. Only one study, an influential paper in the Stanford Law Review (2003) by Ian Ayres and John J. Donohue iii, implies that these laws lead to an increase in crime. We apply an improved version of the Ayres and Donohue method to a more extensive data set. Our analysis, as well as Ayres and Donohue’s when projected beyond a five-year span, indicates that shall-issue laws decrease crime and the costs of crime. Purists in statistical analysis object with some cause to some of methods employed both by Ayres and Donohue and by us. But our paper upgrades Ayres and Donohue, so, until the next study comes along, our paper should neutralize Ayres and Donohue’s “more guns, more crime” conclusion.
Summary and Conclusion Many articles have been published finding that shall-issue laws reduce crime. Only one article, by Ayres and Donohue who employ a model that combines a dummy variable with a post-law trend, claims to find that shall-issue laws increase crime. However, the only way that they can produce the result that shall-issue laws increase crime is to confine the span of analysis to five years. We show, using their own estimates, that if they had extended their analysis by one more year, they would have concluded that these laws reduce crime. Since most states with shallissue laws have had these laws on the books for more than five years, and the law will presumably remain on the books for some time, the only relevant analysis extends beyond five years. We extend their analysis by adding three more years of data, control for the effects of crack cocaine, control for dynamic effects, and correct the standard errors for clustering. We find that there is an initial increase in crime due to passage of the shall-issue law that is dwarfed over time by the decrease in crime associated with the post-law trend. These results are very similar to those of Ayres and Donohue, properly interpreted. The modified Ayres and Donohue model finds that shall-issue laws significantly reduce murder and burglary across all the adopting states. These laws appear to significantly increase assault, and have no net effect on rape, robbery, larceny, or auto theft. However, in the long run only the trend coefficients matter.
We estimate a net benefit of $450 million per year as a result of the passage of these laws.
We also estimate that, up through 2000, there was a cumulative overall net benefit of these laws of $28 billion since their passage.
We think that there is credible statistical evidence that these laws lower the costs of crime. But at the very least, the present study should neutralize any “more guns, more crime” thinking based on Ayres and Donohue’s work in the Stanford Law Review. We acknowledge that, especially in light of the methodological issues of the literature in general, the magnitudes derived from our analysis of crime statistics and the supposed costs of crime might be dwarfed by other considerations in judging the policy issue. Some might contend that allowing individuals to carry a concealed weapon is a moral or cultural bad. Others might contend that greater liberty is a moral or cultural good. All we are confident in saying is that the evidence, such as it is, seems to support the hypothesis that the shall-issue law is generally beneficial with respect to its overall long run effect on crime.
The crime rate in general has deceased
Okay the crime rate in general has deceased. You making this a correlation about gun ownership is based on nothing. There is no direct connection between the two. You’re just pretending there is.A lot of things can be bi-directional. Studies suggest this for this reason. You have no good reason to actually believe that shit. Your confidence is based on nothing. Either way, nothing good comes from more higher gun ownership. Clearly people owning more guns doesn’t stop the crime rate anyway. The result is more bad people with guns.No, it isn't as the article clearly states and I have shown. Increased gun ownership is far more likely to be a result of violent crime than the cause. I doubt you even bothered to read what you linked to and have no idea what it says. That's why I quoted it. But apparently you didn't bother to read that either.It’s linked in the article idiot.SHOW ME THE FUCKING RESEARCH OR FUCK OFF, YAHOO "NEWS"!!!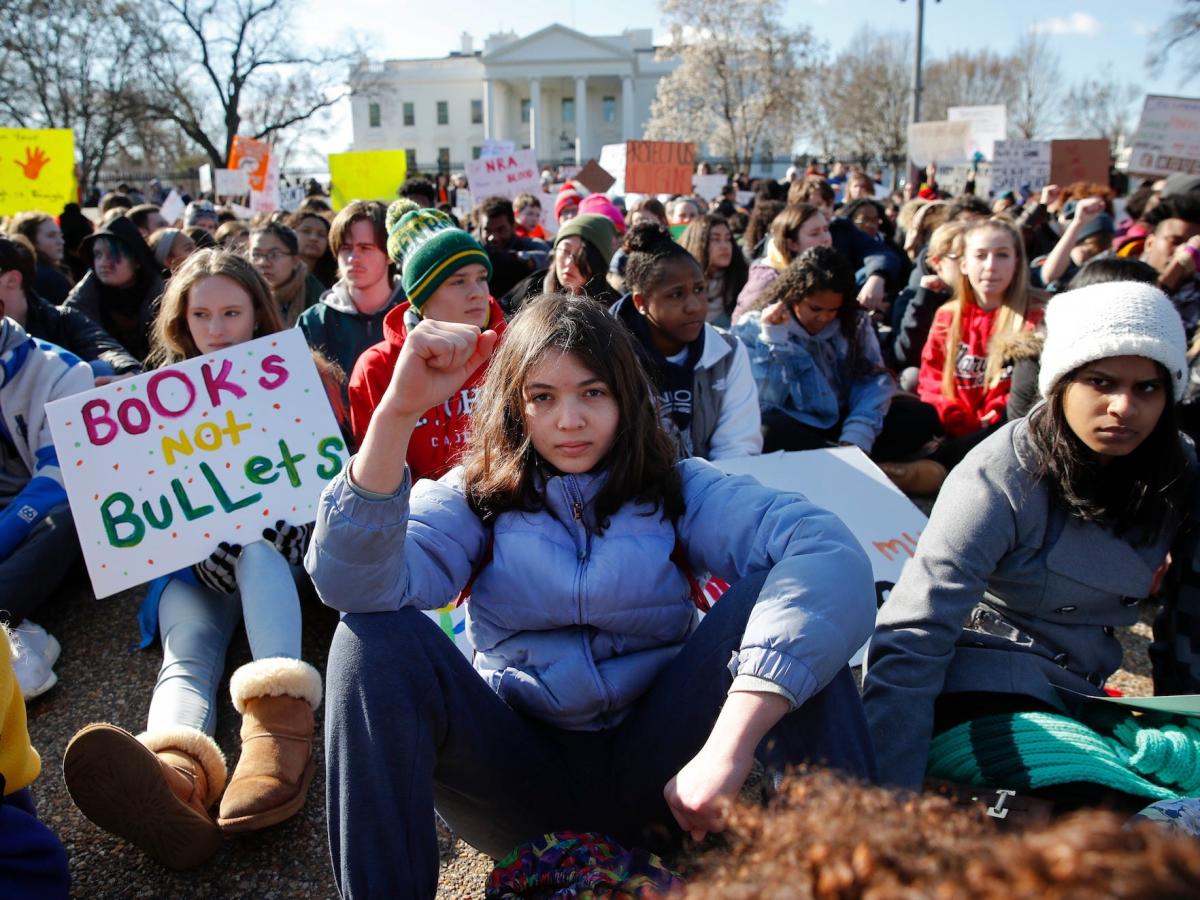
New research puts the 'good guy with a gun' idea to rest: Loose concealed-carry laws are linked to more firearm homicides
States with looser concealed-carry laws have higher rates of gun homicide. And higher gun-ownership rates are associated with more mass shootings.www.yahoo.com
A new study found that states with looser concealed-carry gun laws have higher rates of gun homicide.
The results also showed that higher levels of gun ownership are associated with more mass shootings.
The study suggests the US could reduce gun violence by lowering levels of gun ownership and passing stricter concealed-carry laws.
Visit Business Insider's homepage for more stories.
The "good guy with a gun" theory goes like this: If more well-intentioned people carry guns, there's a higher chance of stopping a violent shooter.
Unfortunately, that's not how it works in real life, according to new research published in the journal Justice Quarterly. The study found that laws allowing more people to carry guns in public are associated with a rise in gun violence. The results also showed that the higher a state's gun-ownership rate, the more likely a mass shooting is.
You are an idiot....27 years of actual increased gun ownership shows.....that normal people who own and carry guns does not increase the gun crime rate....at all....
Over the last 27 years, we went from 200 million guns in private hands in the 1990s and 4.7 million people carrying guns for self defense in 1997...to close to 400-600 million guns in private hands and over 18.6 million people carrying guns for self defense in 2018...guess what happened...
-- gun murder down 49%
--gun crime down 75%
--violent crime down 72%
Gun Homicide Rate Down 49% Since 1993 Peak; Public Unaware
Compared with 1993, the peak of U.S. gun homicides, the firearm homicide rate was 49% lower in 2010, and there were fewer deaths, even though the nation’s population grew. The victimization rate for other violent crimes with a firearm—assaults, robberies and sex crimes—was 75% lower in 2011 than in 1993. Violent non-fatal crime victimization overall (with or without a firearm) also is down markedly (72%) over two decades.
----
Maine tops ‘safest states’ rankings four years after removing major gun restriction
When Maine passed a “Constitutional Carry” law allowing Maine residents to carry a concealed firearm without any special permit in 2015, opponents of the law forecast a dangerous future for the state. They said the new law would hurt public safety and put Maine kids at risk.
One state representative who opposed the bill went so far as to say it would give Mainers a reason to be afraid every time they went out in public or to work.
Another state representative suggested the law would lead to violent criminals with recent arrests and convictions legally carrying handguns.
-----
Now four years later, Maine has been named the safest state in the nation according to US News and World Report’s public safety rankings, which measures the fifty states based on crime data.
Ranking as the top safest state for violent crime and fourth for property crime, Maine edges out another New England state, Vermont, for the top spot. Of note, Vermont also is a “Constitutional Carry” state. New Hampshire ranks third in the national rankings, giving New England all three of the top spots in the nation.
In 2018, Maine was edged out by Vermont in the same “safest states” ranking, but declared the best state overall in the broader “Crime and Corrections” category.
In 2017, using a different methodology, Maine was ranked second among the fifty states in the “Crime and Corrections” category and also second in the categories used to rank the “safest states.”
The U.S. News and World Report “Best States” rankings are built in partnership with McKinsey & Company, a firm that works closely with state leaders around the nation.
Maine has also ranked at the top of other state rankings. WalletHub.com recently ranked Maine second in “Personal and Residential Safety” among the fifty states, and third overall.
=============
Bolsonaro's Brazil, More Legal Guns, Homicide Rates Down Precipitously
In December, 2018, in an article published by the Wall Street Journal, this pronouncement was made. From the wsj.com:
Homicides in Brazil were at historic highs in 2017. They dropped a bit in 2018, as candidate Bolsonaro ran on reform of the gun laws to allow self defense, and reform of the law to get tough on crime. The homicide numbers dropped from 59,000 in 2017, to 51,000 in 2018. President Bolsonaro was elected in October of 2018.Now, Brazil is set to embark on an experiment that will determine what happens when you loosen gun restrictions in a country battling an overpowering wave of gun crime.
After taking office on 1 January, 2019, President Bolsonaro issued his first decree reforming some of Brazil's extreme gun laws on 15 January, 2019. The drop in Brazil's homicide rate accelerated.
-------
Early in the Bolsonaro presidency, a Brazilian lawyer prediceted the homicide rate would drop. From ammoland.com:
The rate reduction was not quite that high. Only 10,000 lives were saved. From wtop.com:César Mello, asked that I include information that early reports are showing a 25% drop in Brazil's homicide rate, in the first quarter of 2019. If this trend continues, 16,000 lives will have been saved in the first year of President Bolsonaro's time in office.
When translated to homicide rates, the rate dropped 17% in 2018, then 23% more in 2019. The population of Brazil in 2019 was 210 million. The rate of homicides per 100,000 was 19.83. That is less than 2/3 of the homicide rate in 2017, which was 30.8.Brazil had 41,635 killings in 2019, down 19% from the prior year and the least number of homicides since 2007, when the so-called Violence Monitor index was launched. It is a partnership between the non-profit Brazilian Forum of Public Security, the University of Sao Paulo’s Center for the Study of Violence, and news website G1, which published the data Friday.
What you’re saying contradicts before anyway lol.
Does the study provide specific examples?Uh no. As the study states, in the areas where gun ownership is higher, mass shootings are more common.Mass shootings always happen where people aren't allowed to carry guns. More gun ownership correlates with gun violence because people living in high crime areas buy guns for protection.Yeah dude. No one ever said people haven’t defended themselves with guns. That is completely besides the point of what this article is saying is that “a good guy with a gun” does nothing to prevent mass shootings. More gun ownership is correlated with more gun violence. These are the facts that matter.Defensive Gun Use Is Not a MythShould I even bother asking for a source?Bullshit. The crime rate went down in every state that adopted concealed carry. It's almost certain the study is based on flawed assumptions.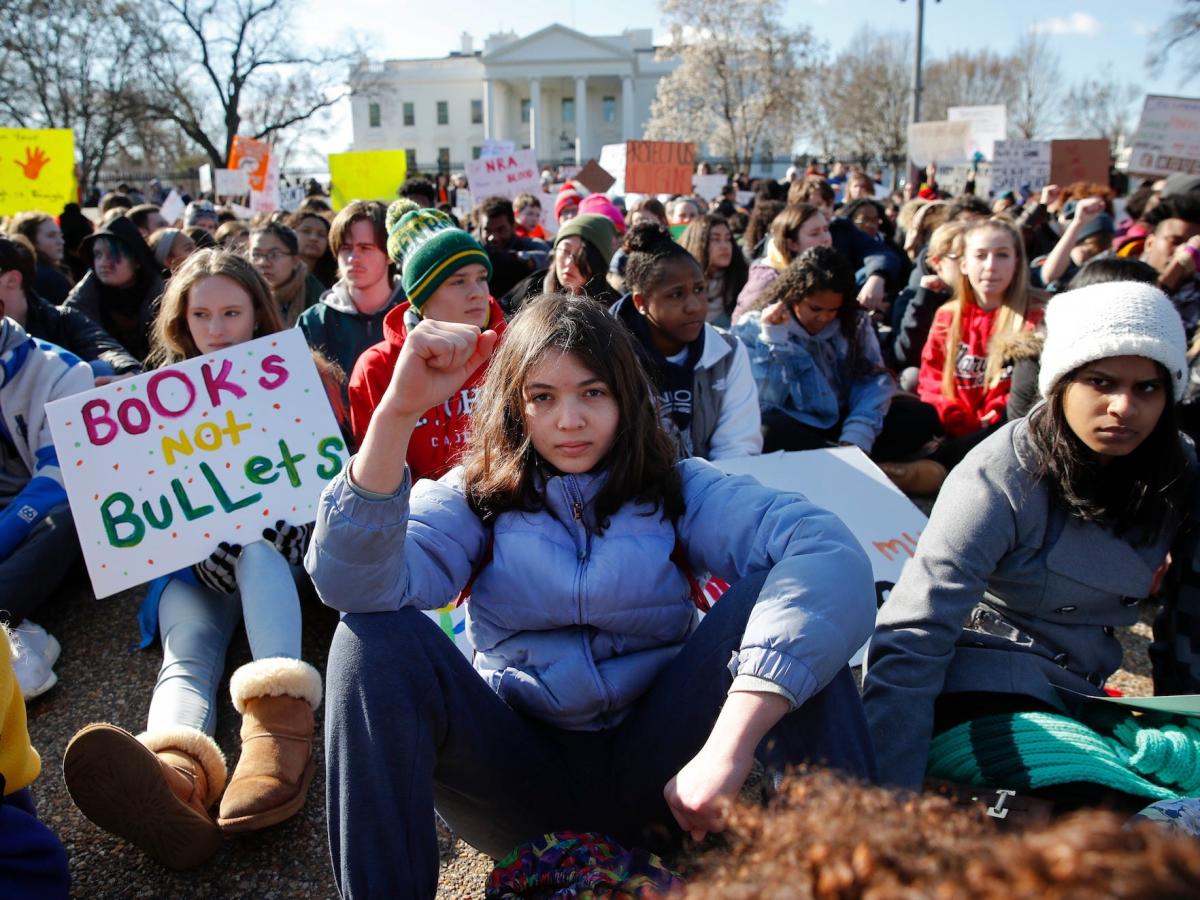
New research puts the 'good guy with a gun' idea to rest: Loose concealed-carry laws are linked to more firearm homicides
States with looser concealed-carry laws have higher rates of gun homicide. And higher gun-ownership rates are associated with more mass shootings.www.yahoo.com
A new study found that states with looser concealed-carry gun laws have higher rates of gun homicide.
The results also showed that higher levels of gun ownership are associated with more mass shootings.
The study suggests the US could reduce gun violence by lowering levels of gun ownership and passing stricter concealed-carry laws.
Visit Business Insider's homepage for more stories.
The "good guy with a gun" theory goes like this: If more well-intentioned people carry guns, there's a higher chance of stopping a violent shooter.
Unfortunately, that's not how it works in real life, according to new research published in the journal Justice Quarterly. The study found that laws allowing more people to carry guns in public are associated with a rise in gun violence. The results also showed that the higher a state's gun-ownership rate, the more likely a mass shooting is.
What a fucking moron.
You can’t even bother with statistics that counter mine.
Again, the point is, moron, that the vast majority of mass shootings ARE NOT prevented by a good guy with a gun. That’s the only point that matters.Lol this study is cherry picking instances where a good guy with a gun happened - a grand total of 25 times lol. Why this doesn’t matter is because the large majority of mass shootings did NOT have a good guy with a gun.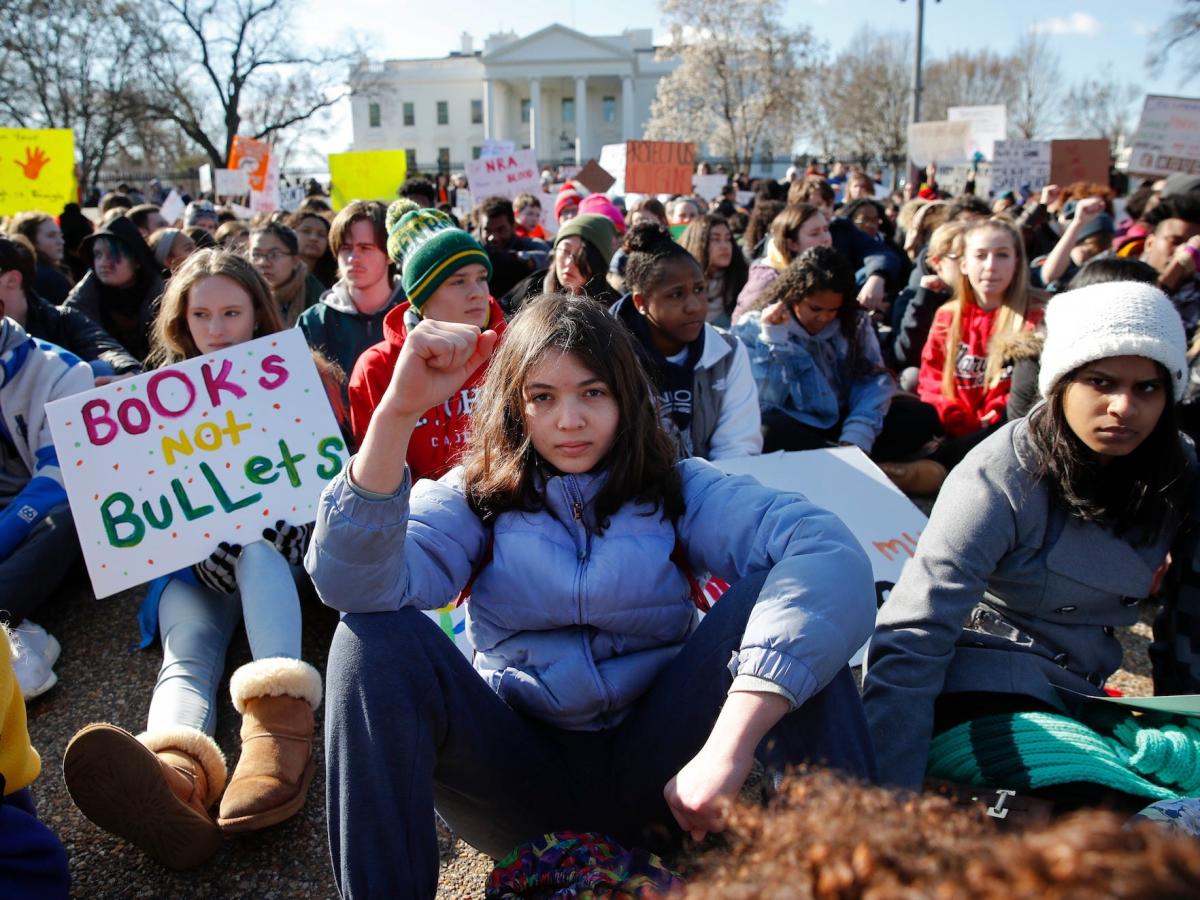
New research puts the 'good guy with a gun' idea to rest: Loose concealed-carry laws are linked to more firearm homicides
States with looser concealed-carry laws have higher rates of gun homicide. And higher gun-ownership rates are associated with more mass shootings.www.yahoo.com
A new study found that states with looser concealed-carry gun laws have higher rates of gun homicide.
The results also showed that higher levels of gun ownership are associated with more mass shootings.
The study suggests the US could reduce gun violence by lowering levels of gun ownership and passing stricter concealed-carry laws.
Visit Business Insider's homepage for more stories.
The "good guy with a gun" theory goes like this: If more well-intentioned people carry guns, there's a higher chance of stopping a violent shooter.
Unfortunately, that's not how it works in real life, according to new research published in the journal Justice Quarterly. The study found that laws allowing more people to carry guns in public are associated with a rise in gun violence. The results also showed that the higher a state's gun-ownership rate, the more likely a mass shooting is.
Here...some actual truth....
Armed Citizens Are Successful 94% Of The Time At Active Shooter Events [FBI]
Of all the active shooter events there were 33 at which an armed citizen was present. Of those, Armed Citizens were successful at stopping the Active shooter 75.8% of the time (25 incidents) and were successful in reducing the loss of life in an additional 18.2% (6) of incidents. In only 2 of the 33 incidents (6.1%) was the Armed Citizen(s) not helpful in any way in stopping the active shooter or reducing the loss of life.
Thus the headline of our report that Armed Citizens Are Successful 94% Of The Time At Active Shooter Events.
In the 2 incidents at which the armed citizen “failed” to stop or slow the active shooter, one is the previously mentioned incident with hunters. The other is an incident in which the CCWer was shot in the back in a Las Vegas Walmart when he failed to identify that there were 2 Active Shooters involved in the attack. He neglected to identify the one that shot him in the back while he was trying to ambush the other perpetrator.
We also decided to look at the breakdown of events that took place in gun free zones and the relative death toll from events in gun free zones vs non-gun-free zones.
Of the 283 incidents in our data pool, we were unable to identify if the event took place in a gun-free zone in a large number (41%) of the events. Most of the events took place at a business, church, home, or other places at which as a rule of law it is not a gun free zone but potentially could have been declared one by the property owner. Without any information in the FBI study or any indication one way or the other from the news reports, we have indicated that event with a question mark.
If you look at all of the Active Shooter events (pie chart on the top) you see that for those which we have the information, almost twice as many took place in gun free zones than not; but realistically the vast majority of those for which we have no information (indicated as ?) are probably NOT gun free zones.
If you isolate just the events at which 8 or more people were killed the data paints a different picture (pie chart on the bottom). In these incidents, 77.8% took place in a gun-free zone suggesting that gun free zones lead to a higher death rate vs active shooter events in general
=====
One of the final metrics we thought was important to consider is the potential tendency for armed citizens to injure or kill innocent people in their attempt to “save the day.” A common point in political discussions is to point out the lack of training of most armed citizens and the decrease in safety inherent in their presence during violent encounters.
As you can see below, however, at the 33 incidents at which Armed Citizens were present, there were zero situations at which the Armed Citizen injured or killed an innocent person. It never happened.
Moron....those are mass public shootings where the good guys had guns.....versus the over 90% of the locations that are gun free zones...you moron.......
When you make almosts every public space a gun free zone, normal, law abiding people will not break the law and carry their guns....so these are mass public shootings that took place in locations where someone had their gun on them......you dumb shit........
You don't know what you are talking about.
Okay again , the violent crime rates across the board have been going down. My study specifically makes the connection between gun ownership and GUN DEATHS SPECIFICALLY. Your so called studies are simply looking at crime trends that have already been going down anyway.A lot of things can be bi-directional. Studies suggest this for this reason. You have no good reason to actually believe that shit. Your confidence is based on nothing. Either way, nothing good comes from more higher gun ownership. Clearly people owning more guns doesn’t stop the crime rate anyway. The result is more bad people with guns.No, it isn't as the article clearly states and I have shown. Increased gun ownership is far more likely to be a result of violent crime than the cause. I doubt you even bothered to read what you linked to and have no idea what it says. That's why I quoted it. But apparently you didn't bother to read that either.It’s linked in the article idiot.SHOW ME THE FUCKING RESEARCH OR FUCK OFF, YAHOO "NEWS"!!!
New research puts the 'good guy with a gun' idea to rest: Loose concealed-carry laws are linked to more firearm homicides
States with looser concealed-carry laws have higher rates of gun homicide. And higher gun-ownership rates are associated with more mass shootings.www.yahoo.com
A new study found that states with looser concealed-carry gun laws have higher rates of gun homicide.
The results also showed that higher levels of gun ownership are associated with more mass shootings.
The study suggests the US could reduce gun violence by lowering levels of gun ownership and passing stricter concealed-carry laws.
Visit Business Insider's homepage for more stories.
The "good guy with a gun" theory goes like this: If more well-intentioned people carry guns, there's a higher chance of stopping a violent shooter.
Unfortunately, that's not how it works in real life, according to new research published in the journal Justice Quarterly. The study found that laws allowing more people to carry guns in public are associated with a rise in gun violence. The results also showed that the higher a state's gun-ownership rate, the more likely a mass shooting is.
Here...actual research proving you wrong...
Right-to-Carry Concealed Weapon Laws and Homicide in Large U.S. Counties: The Effect on Weapon Types, Victim Characteristics, and Victim-Offender Relationships By DAVID E. OLSON AND MICHAEL D. MALTZ, Journal of Law and Economics, October 2001
Our results indicated that the direction of effect of the shall-issue law on total SHR homicide rates was similar to that obtained by Lott and Mustard, although the magnitude of the effect was somewhat smaller and was statistically significant at the 7 percent level. In our analysis, which included only counties with a 1977 population of 100,000 or more, laws allowing for concealed weapons were associated with a 6.52 percent reduction in total homicides (Table 2). By comparison, Lott and Mustard found the concealed weapon dummy variable to be associated with a 7.65 percent reduction in total homicides across all counties and a 9 percent reduction in homicides when only large counties (populations of 100,000 or more) were included.43
====
====http://johnrlott.tripod.com/Plassmann_Whitley.pdf
COMMENTS
Confirming ìMore Guns, Less Crimeî Florenz Plassmann* & John Whitley**
CONCLUSION Analyzing county-level data for the entire United States from 1977 to 2000, we find annual reductions in murder rates between 1.5% and 2.3% for each additional year that a right-to-carry law is in effect.
For the first five years that such a law is in effect, the total benefit from reduced crimes usually ranges between about $2 and $3 billion per year.
The results are very similar to earlier estimates using county-level data from 1977 to 1996. We appreciate the continuing effort that Ayres and Donohue have made in discussing the impact of right-to-carry laws on crime rates. Yet we believe that both the new evidence provided by them as well as our new results show consistently that right-to-carry laws reduce crime and save lives. Unfortunately, a few simple mistakes lead Ayres and Donohue to incorrectly claim that crime rates significantly increase after right-to-carry laws are initially adopted and to misinterpret the significance of their own estimates that examined the year-to-year impact of the law.
http://crimeresearch.org/wp-content...An-Exercise-in-Replication.proof_.revised.pdf
~ The Impact of Right-to-Carry Laws on Crime: An Exercise in Replication1
Carlisle E. Moody College of William and Mary - Department of Economics, Virginia 23187, U.S.A. E-mail: [email protected] Thomas B. Marvell Justec Research, Virginia 23185, U.S.A. Paul R. Zimmerman U.S. Federal Trade Commission - Bureau of Economics, Washington, D.C., U.S.A. Fasil Alemante College of William and Mary, Virginia 23187, U.S.A.
Abstract: In an article published in 2011, Aneja, Donohue and Zhang found that shall-issue or right-to-carry (RTC) concealed weapons laws have no effect on any crime except for a positive effect on assault.
This paper reports a replication of their basic findings and some corresponding robustness checks, which reveal a serious omitted variable problem.
Once corrected for omitted variables, the most robust result, confirmed using both county and state data, is that RTC laws significantly reduce murder.
====
===An examination of the effects of concealed weapons laws and assault weapons bans on state-level murder rates
Mark Gius
Abstract
The purpose of the present study is to determine the effects of state-level assault weapons bans and concealed weapons laws on state-level murder rates.
Using data for the period 1980 to 2009 and controlling for state and year fixed effects, the results of the present study suggest that states with restrictions on the carrying of concealed weapons had higher gun-related murder rates than other states.
It was also found that assault weapons bans did not significantly affect murder rates at the state level. These results suggest that restrictive concealed weapons laws may cause an increase in gun-related murders at the state level. The results of this study are consistent with some prior research in this area, most notably Lott and Mustard (1997).
“The Debate on Shall-Issue Laws” by Carlisle e. Moody and Thomas B. Marvell, published in Econ Journal Watch, volume 5, number 3, September 2008 It is also available here..
Summary and Conclusion
Many articles have been published finding that shall-issue laws reduce crime. Only one article, by Ayres and Donohue who employ a model that combines a dummy variable with a post-law trend, claims to find that shall-issue laws increase crime.
However, the only way that they can produce the result that shall-issue laws increase crime is to confine the span of analysis to five years
. We show, using their own estimates, that if they had extended their analysis by one more year, they would have concluded that these laws reduce crime.
Since most states with shallissue laws have had these laws on the books for more than five years, and the law will presumably remain on the books for some time, the only relevant analysis extends beyond five years. We extend their analysis by adding three more years of data, control for the effects of crack cocaine, control for dynamic effects, and correct the standard errors for clustering.
We find that there is an initial increase in crime due to passage of the shall-issue law that is dwarfed over time by the decrease in crime associated with the post-law trend.
These results are very similar to those of Ayres and Donohue, properly interpreted.
The modified Ayres and Donohue model finds that shall-issue laws significantly reduce murder and burglary across all the adopting states. These laws appear to significantly increase assault, and have no net effect on rape, robbery, larceny, or auto theft. However, in the long run only the trend coefficients matter. We estimate a net benefit of $450 million per year as a result of the passage of these laws. We also estimate that, up through 2000, there was a cumulative overall net benefit of these laws of $28 billion since their passage. We think that there is credible statistical evidence that these laws lower the costs of crime. But at the very least, the present study should neutralize any “more guns, more crime” thinking based on Ayres and Donohue’s work in the Stanford Law Review
Taking apart ayre and donahue one....
“The Debate on Shall-Issue Laws” by Carlisle e. Moody and Thomas B. Marvell, published in Econ Journal Watch, volume 5, number 3, September 2008 It is also available here..
Abstract
“Shall-issue” laws require authorities to issue concealed-weapons permits to anyone who applies, unless the applicant has a criminal record or a history of mental illness. A large number of studies indicate that shall-issue laws reduce crime. Only one study, an influential paper in the Stanford Law Review (2003) by Ian Ayres and John J. Donohue iii, implies that these laws lead to an increase in crime. We apply an improved version of the Ayres and Donohue method to a more extensive data set. Our analysis, as well as Ayres and Donohue’s when projected beyond a five-year span, indicates that shall-issue laws decrease crime and the costs of crime. Purists in statistical analysis object with some cause to some of methods employed both by Ayres and Donohue and by us. But our paper upgrades Ayres and Donohue, so, until the next study comes along, our paper should neutralize Ayres and Donohue’s “more guns, more crime” conclusion.
Summary and Conclusion Many articles have been published finding that shall-issue laws reduce crime. Only one article, by Ayres and Donohue who employ a model that combines a dummy variable with a post-law trend, claims to find that shall-issue laws increase crime. However, the only way that they can produce the result that shall-issue laws increase crime is to confine the span of analysis to five years. We show, using their own estimates, that if they had extended their analysis by one more year, they would have concluded that these laws reduce crime. Since most states with shallissue laws have had these laws on the books for more than five years, and the law will presumably remain on the books for some time, the only relevant analysis extends beyond five years. We extend their analysis by adding three more years of data, control for the effects of crack cocaine, control for dynamic effects, and correct the standard errors for clustering. We find that there is an initial increase in crime due to passage of the shall-issue law that is dwarfed over time by the decrease in crime associated with the post-law trend. These results are very similar to those of Ayres and Donohue, properly interpreted. The modified Ayres and Donohue model finds that shall-issue laws significantly reduce murder and burglary across all the adopting states. These laws appear to significantly increase assault, and have no net effect on rape, robbery, larceny, or auto theft. However, in the long run only the trend coefficients matter.
We estimate a net benefit of $450 million per year as a result of the passage of these laws.
We also estimate that, up through 2000, there was a cumulative overall net benefit of these laws of $28 billion since their passage.
We think that there is credible statistical evidence that these laws lower the costs of crime. But at the very least, the present study should neutralize any “more guns, more crime” thinking based on Ayres and Donohue’s work in the Stanford Law Review. We acknowledge that, especially in light of the methodological issues of the literature in general, the magnitudes derived from our analysis of crime statistics and the supposed costs of crime might be dwarfed by other considerations in judging the policy issue. Some might contend that allowing individuals to carry a concealed weapon is a moral or cultural bad. Others might contend that greater liberty is a moral or cultural good. All we are confident in saying is that the evidence, such as it is, seems to support the hypothesis that the shall-issue law is generally beneficial with respect to its overall long run effect on crime.
Okay again , the violent crime rates across the board have been going down. My study specifically makes the connection between gun ownership and GUN DEATHS SPECIFICALLY. Your so called studies are simply looking at crime trends that have already been going down anyway.A lot of things can be bi-directional. Studies suggest this for this reason. You have no good reason to actually believe that shit. Your confidence is based on nothing. Either way, nothing good comes from more higher gun ownership. Clearly people owning more guns doesn’t stop the crime rate anyway. The result is more bad people with guns.No, it isn't as the article clearly states and I have shown. Increased gun ownership is far more likely to be a result of violent crime than the cause. I doubt you even bothered to read what you linked to and have no idea what it says. That's why I quoted it. But apparently you didn't bother to read that either.It’s linked in the article idiot.SHOW ME THE FUCKING RESEARCH OR FUCK OFF, YAHOO "NEWS"!!!
New research puts the 'good guy with a gun' idea to rest: Loose concealed-carry laws are linked to more firearm homicides
States with looser concealed-carry laws have higher rates of gun homicide. And higher gun-ownership rates are associated with more mass shootings.www.yahoo.com
A new study found that states with looser concealed-carry gun laws have higher rates of gun homicide.
The results also showed that higher levels of gun ownership are associated with more mass shootings.
The study suggests the US could reduce gun violence by lowering levels of gun ownership and passing stricter concealed-carry laws.
Visit Business Insider's homepage for more stories.
The "good guy with a gun" theory goes like this: If more well-intentioned people carry guns, there's a higher chance of stopping a violent shooter.
Unfortunately, that's not how it works in real life, according to new research published in the journal Justice Quarterly. The study found that laws allowing more people to carry guns in public are associated with a rise in gun violence. The results also showed that the higher a state's gun-ownership rate, the more likely a mass shooting is.
Here...actual research proving you wrong...
Right-to-Carry Concealed Weapon Laws and Homicide in Large U.S. Counties: The Effect on Weapon Types, Victim Characteristics, and Victim-Offender Relationships By DAVID E. OLSON AND MICHAEL D. MALTZ, Journal of Law and Economics, October 2001
Our results indicated that the direction of effect of the shall-issue law on total SHR homicide rates was similar to that obtained by Lott and Mustard, although the magnitude of the effect was somewhat smaller and was statistically significant at the 7 percent level. In our analysis, which included only counties with a 1977 population of 100,000 or more, laws allowing for concealed weapons were associated with a 6.52 percent reduction in total homicides (Table 2). By comparison, Lott and Mustard found the concealed weapon dummy variable to be associated with a 7.65 percent reduction in total homicides across all counties and a 9 percent reduction in homicides when only large counties (populations of 100,000 or more) were included.43
====
====http://johnrlott.tripod.com/Plassmann_Whitley.pdf
COMMENTS
Confirming ìMore Guns, Less Crimeî Florenz Plassmann* & John Whitley**
CONCLUSION Analyzing county-level data for the entire United States from 1977 to 2000, we find annual reductions in murder rates between 1.5% and 2.3% for each additional year that a right-to-carry law is in effect.
For the first five years that such a law is in effect, the total benefit from reduced crimes usually ranges between about $2 and $3 billion per year.
The results are very similar to earlier estimates using county-level data from 1977 to 1996. We appreciate the continuing effort that Ayres and Donohue have made in discussing the impact of right-to-carry laws on crime rates. Yet we believe that both the new evidence provided by them as well as our new results show consistently that right-to-carry laws reduce crime and save lives. Unfortunately, a few simple mistakes lead Ayres and Donohue to incorrectly claim that crime rates significantly increase after right-to-carry laws are initially adopted and to misinterpret the significance of their own estimates that examined the year-to-year impact of the law.
http://crimeresearch.org/wp-content...An-Exercise-in-Replication.proof_.revised.pdf
~ The Impact of Right-to-Carry Laws on Crime: An Exercise in Replication1
Carlisle E. Moody College of William and Mary - Department of Economics, Virginia 23187, U.S.A. E-mail: [email protected] Thomas B. Marvell Justec Research, Virginia 23185, U.S.A. Paul R. Zimmerman U.S. Federal Trade Commission - Bureau of Economics, Washington, D.C., U.S.A. Fasil Alemante College of William and Mary, Virginia 23187, U.S.A.
Abstract: In an article published in 2011, Aneja, Donohue and Zhang found that shall-issue or right-to-carry (RTC) concealed weapons laws have no effect on any crime except for a positive effect on assault.
This paper reports a replication of their basic findings and some corresponding robustness checks, which reveal a serious omitted variable problem.
Once corrected for omitted variables, the most robust result, confirmed using both county and state data, is that RTC laws significantly reduce murder.
====
===An examination of the effects of concealed weapons laws and assault weapons bans on state-level murder rates
Mark Gius
Abstract
The purpose of the present study is to determine the effects of state-level assault weapons bans and concealed weapons laws on state-level murder rates.
Using data for the period 1980 to 2009 and controlling for state and year fixed effects, the results of the present study suggest that states with restrictions on the carrying of concealed weapons had higher gun-related murder rates than other states.
It was also found that assault weapons bans did not significantly affect murder rates at the state level. These results suggest that restrictive concealed weapons laws may cause an increase in gun-related murders at the state level. The results of this study are consistent with some prior research in this area, most notably Lott and Mustard (1997).
“The Debate on Shall-Issue Laws” by Carlisle e. Moody and Thomas B. Marvell, published in Econ Journal Watch, volume 5, number 3, September 2008 It is also available here..
Summary and Conclusion
Many articles have been published finding that shall-issue laws reduce crime. Only one article, by Ayres and Donohue who employ a model that combines a dummy variable with a post-law trend, claims to find that shall-issue laws increase crime.
However, the only way that they can produce the result that shall-issue laws increase crime is to confine the span of analysis to five years
. We show, using their own estimates, that if they had extended their analysis by one more year, they would have concluded that these laws reduce crime.
Since most states with shallissue laws have had these laws on the books for more than five years, and the law will presumably remain on the books for some time, the only relevant analysis extends beyond five years. We extend their analysis by adding three more years of data, control for the effects of crack cocaine, control for dynamic effects, and correct the standard errors for clustering.
We find that there is an initial increase in crime due to passage of the shall-issue law that is dwarfed over time by the decrease in crime associated with the post-law trend.
These results are very similar to those of Ayres and Donohue, properly interpreted.
The modified Ayres and Donohue model finds that shall-issue laws significantly reduce murder and burglary across all the adopting states. These laws appear to significantly increase assault, and have no net effect on rape, robbery, larceny, or auto theft. However, in the long run only the trend coefficients matter. We estimate a net benefit of $450 million per year as a result of the passage of these laws. We also estimate that, up through 2000, there was a cumulative overall net benefit of these laws of $28 billion since their passage. We think that there is credible statistical evidence that these laws lower the costs of crime. But at the very least, the present study should neutralize any “more guns, more crime” thinking based on Ayres and Donohue’s work in the Stanford Law Review
Taking apart ayre and donahue one....
“The Debate on Shall-Issue Laws” by Carlisle e. Moody and Thomas B. Marvell, published in Econ Journal Watch, volume 5, number 3, September 2008 It is also available here..
Abstract
“Shall-issue” laws require authorities to issue concealed-weapons permits to anyone who applies, unless the applicant has a criminal record or a history of mental illness. A large number of studies indicate that shall-issue laws reduce crime. Only one study, an influential paper in the Stanford Law Review (2003) by Ian Ayres and John J. Donohue iii, implies that these laws lead to an increase in crime. We apply an improved version of the Ayres and Donohue method to a more extensive data set. Our analysis, as well as Ayres and Donohue’s when projected beyond a five-year span, indicates that shall-issue laws decrease crime and the costs of crime. Purists in statistical analysis object with some cause to some of methods employed both by Ayres and Donohue and by us. But our paper upgrades Ayres and Donohue, so, until the next study comes along, our paper should neutralize Ayres and Donohue’s “more guns, more crime” conclusion.
Summary and Conclusion Many articles have been published finding that shall-issue laws reduce crime. Only one article, by Ayres and Donohue who employ a model that combines a dummy variable with a post-law trend, claims to find that shall-issue laws increase crime. However, the only way that they can produce the result that shall-issue laws increase crime is to confine the span of analysis to five years. We show, using their own estimates, that if they had extended their analysis by one more year, they would have concluded that these laws reduce crime. Since most states with shallissue laws have had these laws on the books for more than five years, and the law will presumably remain on the books for some time, the only relevant analysis extends beyond five years. We extend their analysis by adding three more years of data, control for the effects of crack cocaine, control for dynamic effects, and correct the standard errors for clustering. We find that there is an initial increase in crime due to passage of the shall-issue law that is dwarfed over time by the decrease in crime associated with the post-law trend. These results are very similar to those of Ayres and Donohue, properly interpreted. The modified Ayres and Donohue model finds that shall-issue laws significantly reduce murder and burglary across all the adopting states. These laws appear to significantly increase assault, and have no net effect on rape, robbery, larceny, or auto theft. However, in the long run only the trend coefficients matter.
We estimate a net benefit of $450 million per year as a result of the passage of these laws.
We also estimate that, up through 2000, there was a cumulative overall net benefit of these laws of $28 billion since their passage.
We think that there is credible statistical evidence that these laws lower the costs of crime. But at the very least, the present study should neutralize any “more guns, more crime” thinking based on Ayres and Donohue’s work in the Stanford Law Review. We acknowledge that, especially in light of the methodological issues of the literature in general, the magnitudes derived from our analysis of crime statistics and the supposed costs of crime might be dwarfed by other considerations in judging the policy issue. Some might contend that allowing individuals to carry a concealed weapon is a moral or cultural bad. Others might contend that greater liberty is a moral or cultural good. All we are confident in saying is that the evidence, such as it is, seems to support the hypothesis that the shall-issue law is generally beneficial with respect to its overall long run effect on crime.
What you’re comparing is the national crime rate that’s been going down in the grand scheme. What my study showed is that in specific areas with more gun ownership, gun deaths are higher. That is the nuance you are missing.Okay the crime rate in general has deceased. You making this a correlation about gun ownership is based on nothing. There is no direct connection between the two. You’re just pretending there is.A lot of things can be bi-directional. Studies suggest this for this reason. You have no good reason to actually believe that shit. Your confidence is based on nothing. Either way, nothing good comes from more higher gun ownership. Clearly people owning more guns doesn’t stop the crime rate anyway. The result is more bad people with guns.No, it isn't as the article clearly states and I have shown. Increased gun ownership is far more likely to be a result of violent crime than the cause. I doubt you even bothered to read what you linked to and have no idea what it says. That's why I quoted it. But apparently you didn't bother to read that either.It’s linked in the article idiot.SHOW ME THE FUCKING RESEARCH OR FUCK OFF, YAHOO "NEWS"!!!
New research puts the 'good guy with a gun' idea to rest: Loose concealed-carry laws are linked to more firearm homicides
States with looser concealed-carry laws have higher rates of gun homicide. And higher gun-ownership rates are associated with more mass shootings.www.yahoo.com
A new study found that states with looser concealed-carry gun laws have higher rates of gun homicide.
The results also showed that higher levels of gun ownership are associated with more mass shootings.
The study suggests the US could reduce gun violence by lowering levels of gun ownership and passing stricter concealed-carry laws.
Visit Business Insider's homepage for more stories.
The "good guy with a gun" theory goes like this: If more well-intentioned people carry guns, there's a higher chance of stopping a violent shooter.
Unfortunately, that's not how it works in real life, according to new research published in the journal Justice Quarterly. The study found that laws allowing more people to carry guns in public are associated with a rise in gun violence. The results also showed that the higher a state's gun-ownership rate, the more likely a mass shooting is.
You are an idiot....27 years of actual increased gun ownership shows.....that normal people who own and carry guns does not increase the gun crime rate....at all....
Over the last 27 years, we went from 200 million guns in private hands in the 1990s and 4.7 million people carrying guns for self defense in 1997...to close to 400-600 million guns in private hands and over 18.6 million people carrying guns for self defense in 2018...guess what happened...
-- gun murder down 49%
--gun crime down 75%
--violent crime down 72%
Gun Homicide Rate Down 49% Since 1993 Peak; Public Unaware
Compared with 1993, the peak of U.S. gun homicides, the firearm homicide rate was 49% lower in 2010, and there were fewer deaths, even though the nation’s population grew. The victimization rate for other violent crimes with a firearm—assaults, robberies and sex crimes—was 75% lower in 2011 than in 1993. Violent non-fatal crime victimization overall (with or without a firearm) also is down markedly (72%) over two decades.
----
Maine tops ‘safest states’ rankings four years after removing major gun restriction
When Maine passed a “Constitutional Carry” law allowing Maine residents to carry a concealed firearm without any special permit in 2015, opponents of the law forecast a dangerous future for the state. They said the new law would hurt public safety and put Maine kids at risk.
One state representative who opposed the bill went so far as to say it would give Mainers a reason to be afraid every time they went out in public or to work.
Another state representative suggested the law would lead to violent criminals with recent arrests and convictions legally carrying handguns.
-----
Now four years later, Maine has been named the safest state in the nation according to US News and World Report’s public safety rankings, which measures the fifty states based on crime data.
Ranking as the top safest state for violent crime and fourth for property crime, Maine edges out another New England state, Vermont, for the top spot. Of note, Vermont also is a “Constitutional Carry” state. New Hampshire ranks third in the national rankings, giving New England all three of the top spots in the nation.
In 2018, Maine was edged out by Vermont in the same “safest states” ranking, but declared the best state overall in the broader “Crime and Corrections” category.
In 2017, using a different methodology, Maine was ranked second among the fifty states in the “Crime and Corrections” category and also second in the categories used to rank the “safest states.”
The U.S. News and World Report “Best States” rankings are built in partnership with McKinsey & Company, a firm that works closely with state leaders around the nation.
Maine has also ranked at the top of other state rankings. WalletHub.com recently ranked Maine second in “Personal and Residential Safety” among the fifty states, and third overall.
=============
Bolsonaro's Brazil, More Legal Guns, Homicide Rates Down Precipitously
In December, 2018, in an article published by the Wall Street Journal, this pronouncement was made. From the wsj.com:
Homicides in Brazil were at historic highs in 2017. They dropped a bit in 2018, as candidate Bolsonaro ran on reform of the gun laws to allow self defense, and reform of the law to get tough on crime. The homicide numbers dropped from 59,000 in 2017, to 51,000 in 2018. President Bolsonaro was elected in October of 2018.Now, Brazil is set to embark on an experiment that will determine what happens when you loosen gun restrictions in a country battling an overpowering wave of gun crime.
After taking office on 1 January, 2019, President Bolsonaro issued his first decree reforming some of Brazil's extreme gun laws on 15 January, 2019. The drop in Brazil's homicide rate accelerated.
-------
Early in the Bolsonaro presidency, a Brazilian lawyer prediceted the homicide rate would drop. From ammoland.com:
The rate reduction was not quite that high. Only 10,000 lives were saved. From wtop.com:César Mello, asked that I include information that early reports are showing a 25% drop in Brazil's homicide rate, in the first quarter of 2019. If this trend continues, 16,000 lives will have been saved in the first year of President Bolsonaro's time in office.
When translated to homicide rates, the rate dropped 17% in 2018, then 23% more in 2019. The population of Brazil in 2019 was 210 million. The rate of homicides per 100,000 was 19.83. That is less than 2/3 of the homicide rate in 2017, which was 30.8.Brazil had 41,635 killings in 2019, down 19% from the prior year and the least number of homicides since 2007, when the so-called Violence Monitor index was launched. It is a partnership between the non-profit Brazilian Forum of Public Security, the University of Sao Paulo’s Center for the Study of Violence, and news website G1, which published the data Friday.
What you’re saying contradicts before anyway lol.
Moron, I am not making that correlation with the Pew study....I make that with the other studies that I posted.
What the Pew research shows is that your theory that more guns create more gun crimes is not based in actual experience, facts or reality...
Over 27 years as more Americans went out, bought guns, and now over 18.6 million people carry those guns for self defense....our gun crime rate went down 75%...it did not go up...which is what you claim would happen....and it didn't happen,
You can't explain that.
Over 27 years as more Americans own and carry guns for self defense the gun murder rate did not go up as you said it would.....it went down by 49%.....something you say can't happen...but it did.....
You can't explain that....
Again, the point is, moron, that the vast majority of mass shootings ARE NOT prevented by a good guy with a gun. That’s the only point that matters.Lol this study is cherry picking instances where a good guy with a gun happened - a grand total of 25 times lol. Why this doesn’t matter is because the large majority of mass shootings did NOT have a good guy with a gun.
New research puts the 'good guy with a gun' idea to rest: Loose concealed-carry laws are linked to more firearm homicides
States with looser concealed-carry laws have higher rates of gun homicide. And higher gun-ownership rates are associated with more mass shootings.www.yahoo.com
A new study found that states with looser concealed-carry gun laws have higher rates of gun homicide.
The results also showed that higher levels of gun ownership are associated with more mass shootings.
The study suggests the US could reduce gun violence by lowering levels of gun ownership and passing stricter concealed-carry laws.
Visit Business Insider's homepage for more stories.
The "good guy with a gun" theory goes like this: If more well-intentioned people carry guns, there's a higher chance of stopping a violent shooter.
Unfortunately, that's not how it works in real life, according to new research published in the journal Justice Quarterly. The study found that laws allowing more people to carry guns in public are associated with a rise in gun violence. The results also showed that the higher a state's gun-ownership rate, the more likely a mass shooting is.
Here...some actual truth....
Armed Citizens Are Successful 94% Of The Time At Active Shooter Events [FBI]
Of all the active shooter events there were 33 at which an armed citizen was present. Of those, Armed Citizens were successful at stopping the Active shooter 75.8% of the time (25 incidents) and were successful in reducing the loss of life in an additional 18.2% (6) of incidents. In only 2 of the 33 incidents (6.1%) was the Armed Citizen(s) not helpful in any way in stopping the active shooter or reducing the loss of life.
Thus the headline of our report that Armed Citizens Are Successful 94% Of The Time At Active Shooter Events.
In the 2 incidents at which the armed citizen “failed” to stop or slow the active shooter, one is the previously mentioned incident with hunters. The other is an incident in which the CCWer was shot in the back in a Las Vegas Walmart when he failed to identify that there were 2 Active Shooters involved in the attack. He neglected to identify the one that shot him in the back while he was trying to ambush the other perpetrator.
We also decided to look at the breakdown of events that took place in gun free zones and the relative death toll from events in gun free zones vs non-gun-free zones.
Of the 283 incidents in our data pool, we were unable to identify if the event took place in a gun-free zone in a large number (41%) of the events. Most of the events took place at a business, church, home, or other places at which as a rule of law it is not a gun free zone but potentially could have been declared one by the property owner. Without any information in the FBI study or any indication one way or the other from the news reports, we have indicated that event with a question mark.
If you look at all of the Active Shooter events (pie chart on the top) you see that for those which we have the information, almost twice as many took place in gun free zones than not; but realistically the vast majority of those for which we have no information (indicated as ?) are probably NOT gun free zones.
If you isolate just the events at which 8 or more people were killed the data paints a different picture (pie chart on the bottom). In these incidents, 77.8% took place in a gun-free zone suggesting that gun free zones lead to a higher death rate vs active shooter events in general
=====
One of the final metrics we thought was important to consider is the potential tendency for armed citizens to injure or kill innocent people in their attempt to “save the day.” A common point in political discussions is to point out the lack of training of most armed citizens and the decrease in safety inherent in their presence during violent encounters.
As you can see below, however, at the 33 incidents at which Armed Citizens were present, there were zero situations at which the Armed Citizen injured or killed an innocent person. It never happened.
Moron....those are mass public shootings where the good guys had guns.....versus the over 90% of the locations that are gun free zones...you moron.......
When you make almosts every public space a gun free zone, normal, law abiding people will not break the law and carry their guns....so these are mass public shootings that took place in locations where someone had their gun on them......you dumb shit........
You don't know what you are talking about.
What you’re comparing is the national crime rate that’s been going down in the grand scheme. What my study showed is that in specific areas with more gun ownership, gun deaths are higher. That is the nuance you are missing.Okay the crime rate in general has deceased. You making this a correlation about gun ownership is based on nothing. There is no direct connection between the two. You’re just pretending there is.A lot of things can be bi-directional. Studies suggest this for this reason. You have no good reason to actually believe that shit. Your confidence is based on nothing. Either way, nothing good comes from more higher gun ownership. Clearly people owning more guns doesn’t stop the crime rate anyway. The result is more bad people with guns.No, it isn't as the article clearly states and I have shown. Increased gun ownership is far more likely to be a result of violent crime than the cause. I doubt you even bothered to read what you linked to and have no idea what it says. That's why I quoted it. But apparently you didn't bother to read that either.It’s linked in the article idiot.SHOW ME THE FUCKING RESEARCH OR FUCK OFF, YAHOO "NEWS"!!!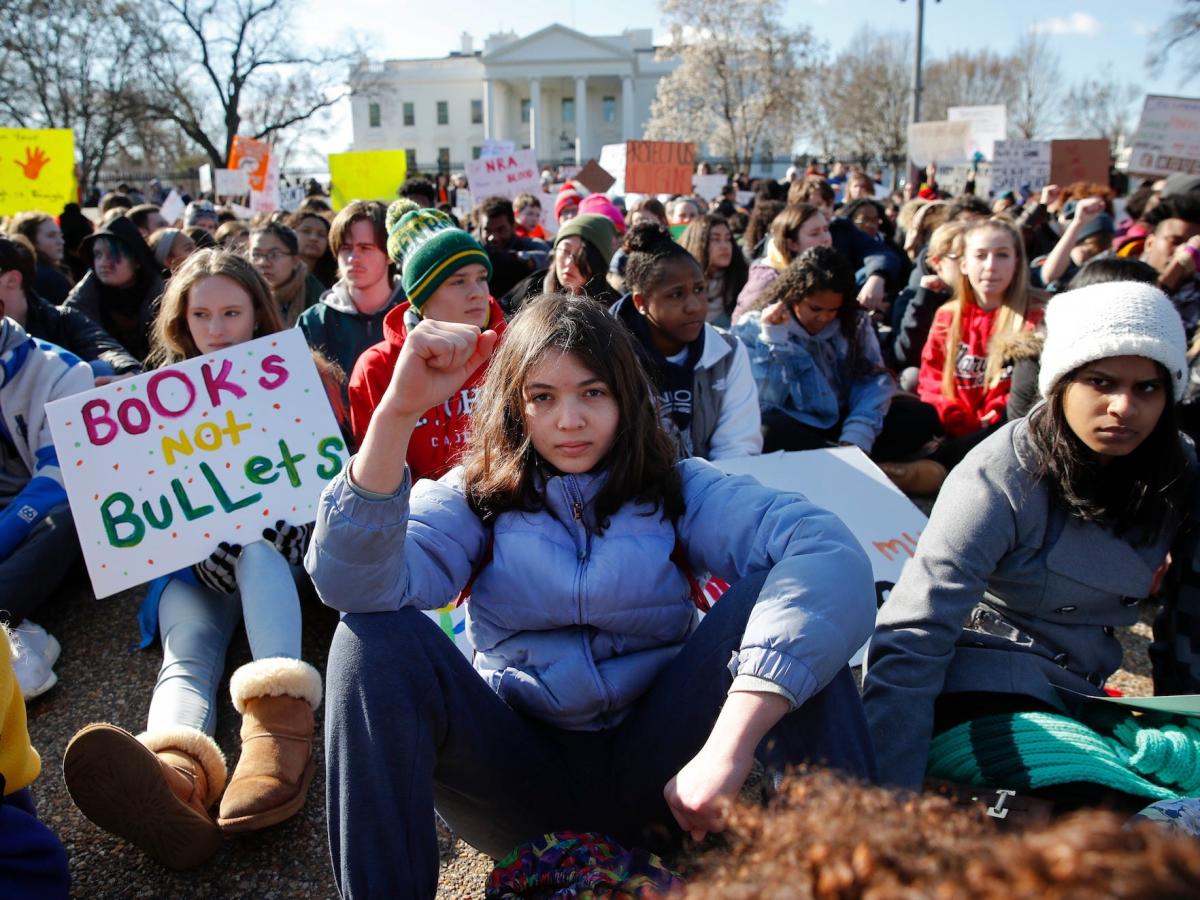
New research puts the 'good guy with a gun' idea to rest: Loose concealed-carry laws are linked to more firearm homicides
States with looser concealed-carry laws have higher rates of gun homicide. And higher gun-ownership rates are associated with more mass shootings.www.yahoo.com
A new study found that states with looser concealed-carry gun laws have higher rates of gun homicide.
The results also showed that higher levels of gun ownership are associated with more mass shootings.
The study suggests the US could reduce gun violence by lowering levels of gun ownership and passing stricter concealed-carry laws.
Visit Business Insider's homepage for more stories.
The "good guy with a gun" theory goes like this: If more well-intentioned people carry guns, there's a higher chance of stopping a violent shooter.
Unfortunately, that's not how it works in real life, according to new research published in the journal Justice Quarterly. The study found that laws allowing more people to carry guns in public are associated with a rise in gun violence. The results also showed that the higher a state's gun-ownership rate, the more likely a mass shooting is.
You are an idiot....27 years of actual increased gun ownership shows.....that normal people who own and carry guns does not increase the gun crime rate....at all....
Over the last 27 years, we went from 200 million guns in private hands in the 1990s and 4.7 million people carrying guns for self defense in 1997...to close to 400-600 million guns in private hands and over 18.6 million people carrying guns for self defense in 2018...guess what happened...
-- gun murder down 49%
--gun crime down 75%
--violent crime down 72%
Gun Homicide Rate Down 49% Since 1993 Peak; Public Unaware
Compared with 1993, the peak of U.S. gun homicides, the firearm homicide rate was 49% lower in 2010, and there were fewer deaths, even though the nation’s population grew. The victimization rate for other violent crimes with a firearm—assaults, robberies and sex crimes—was 75% lower in 2011 than in 1993. Violent non-fatal crime victimization overall (with or without a firearm) also is down markedly (72%) over two decades.
----
Maine tops ‘safest states’ rankings four years after removing major gun restriction
When Maine passed a “Constitutional Carry” law allowing Maine residents to carry a concealed firearm without any special permit in 2015, opponents of the law forecast a dangerous future for the state. They said the new law would hurt public safety and put Maine kids at risk.
One state representative who opposed the bill went so far as to say it would give Mainers a reason to be afraid every time they went out in public or to work.
Another state representative suggested the law would lead to violent criminals with recent arrests and convictions legally carrying handguns.
-----
Now four years later, Maine has been named the safest state in the nation according to US News and World Report’s public safety rankings, which measures the fifty states based on crime data.
Ranking as the top safest state for violent crime and fourth for property crime, Maine edges out another New England state, Vermont, for the top spot. Of note, Vermont also is a “Constitutional Carry” state. New Hampshire ranks third in the national rankings, giving New England all three of the top spots in the nation.
In 2018, Maine was edged out by Vermont in the same “safest states” ranking, but declared the best state overall in the broader “Crime and Corrections” category.
In 2017, using a different methodology, Maine was ranked second among the fifty states in the “Crime and Corrections” category and also second in the categories used to rank the “safest states.”
The U.S. News and World Report “Best States” rankings are built in partnership with McKinsey & Company, a firm that works closely with state leaders around the nation.
Maine has also ranked at the top of other state rankings. WalletHub.com recently ranked Maine second in “Personal and Residential Safety” among the fifty states, and third overall.
=============
Bolsonaro's Brazil, More Legal Guns, Homicide Rates Down Precipitously
In December, 2018, in an article published by the Wall Street Journal, this pronouncement was made. From the wsj.com:
Homicides in Brazil were at historic highs in 2017. They dropped a bit in 2018, as candidate Bolsonaro ran on reform of the gun laws to allow self defense, and reform of the law to get tough on crime. The homicide numbers dropped from 59,000 in 2017, to 51,000 in 2018. President Bolsonaro was elected in October of 2018.Now, Brazil is set to embark on an experiment that will determine what happens when you loosen gun restrictions in a country battling an overpowering wave of gun crime.
After taking office on 1 January, 2019, President Bolsonaro issued his first decree reforming some of Brazil's extreme gun laws on 15 January, 2019. The drop in Brazil's homicide rate accelerated.
-------
Early in the Bolsonaro presidency, a Brazilian lawyer prediceted the homicide rate would drop. From ammoland.com:
The rate reduction was not quite that high. Only 10,000 lives were saved. From wtop.com:César Mello, asked that I include information that early reports are showing a 25% drop in Brazil's homicide rate, in the first quarter of 2019. If this trend continues, 16,000 lives will have been saved in the first year of President Bolsonaro's time in office.
When translated to homicide rates, the rate dropped 17% in 2018, then 23% more in 2019. The population of Brazil in 2019 was 210 million. The rate of homicides per 100,000 was 19.83. That is less than 2/3 of the homicide rate in 2017, which was 30.8.Brazil had 41,635 killings in 2019, down 19% from the prior year and the least number of homicides since 2007, when the so-called Violence Monitor index was launched. It is a partnership between the non-profit Brazilian Forum of Public Security, the University of Sao Paulo’s Center for the Study of Violence, and news website G1, which published the data Friday.
What you’re saying contradicts before anyway lol.
Moron, I am not making that correlation with the Pew study....I make that with the other studies that I posted.
What the Pew research shows is that your theory that more guns create more gun crimes is not based in actual experience, facts or reality...
Over 27 years as more Americans went out, bought guns, and now over 18.6 million people carry those guns for self defense....our gun crime rate went down 75%...it did not go up...which is what you claim would happen....and it didn't happen,
You can't explain that.
Over 27 years as more Americans own and carry guns for self defense the gun murder rate did not go up as you said it would.....it went down by 49%.....something you say can't happen...but it did.....
You can't explain that....
What the article says is that looser concealed carry laws contribute to more gun deaths in general - not just mass shootings. As a separate point, it says the good guy with a gun idea doesn’t affect mass shootings.Okay again , the violent crime rates across the board have been going down. My study specifically makes the connection between gun ownership and GUN DEATHS SPECIFICALLY. Your so called studies are simply looking at crime trends that have already been going down anyway.A lot of things can be bi-directional. Studies suggest this for this reason. You have no good reason to actually believe that shit. Your confidence is based on nothing. Either way, nothing good comes from more higher gun ownership. Clearly people owning more guns doesn’t stop the crime rate anyway. The result is more bad people with guns.No, it isn't as the article clearly states and I have shown. Increased gun ownership is far more likely to be a result of violent crime than the cause. I doubt you even bothered to read what you linked to and have no idea what it says. That's why I quoted it. But apparently you didn't bother to read that either.It’s linked in the article idiot.SHOW ME THE FUCKING RESEARCH OR FUCK OFF, YAHOO "NEWS"!!!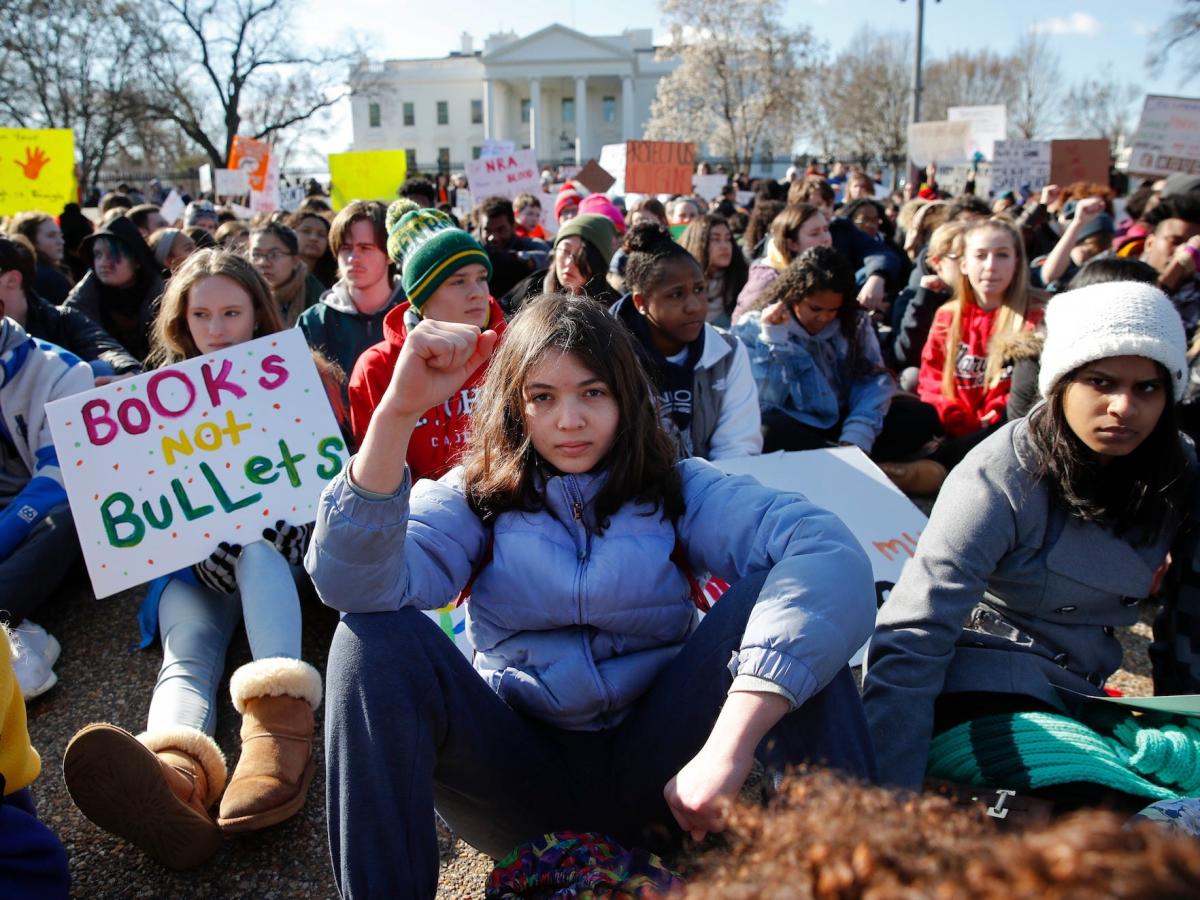
New research puts the 'good guy with a gun' idea to rest: Loose concealed-carry laws are linked to more firearm homicides
States with looser concealed-carry laws have higher rates of gun homicide. And higher gun-ownership rates are associated with more mass shootings.www.yahoo.com
A new study found that states with looser concealed-carry gun laws have higher rates of gun homicide.
The results also showed that higher levels of gun ownership are associated with more mass shootings.
The study suggests the US could reduce gun violence by lowering levels of gun ownership and passing stricter concealed-carry laws.
Visit Business Insider's homepage for more stories.
The "good guy with a gun" theory goes like this: If more well-intentioned people carry guns, there's a higher chance of stopping a violent shooter.
Unfortunately, that's not how it works in real life, according to new research published in the journal Justice Quarterly. The study found that laws allowing more people to carry guns in public are associated with a rise in gun violence. The results also showed that the higher a state's gun-ownership rate, the more likely a mass shooting is.
Here...actual research proving you wrong...
Right-to-Carry Concealed Weapon Laws and Homicide in Large U.S. Counties: The Effect on Weapon Types, Victim Characteristics, and Victim-Offender Relationships By DAVID E. OLSON AND MICHAEL D. MALTZ, Journal of Law and Economics, October 2001
Our results indicated that the direction of effect of the shall-issue law on total SHR homicide rates was similar to that obtained by Lott and Mustard, although the magnitude of the effect was somewhat smaller and was statistically significant at the 7 percent level. In our analysis, which included only counties with a 1977 population of 100,000 or more, laws allowing for concealed weapons were associated with a 6.52 percent reduction in total homicides (Table 2). By comparison, Lott and Mustard found the concealed weapon dummy variable to be associated with a 7.65 percent reduction in total homicides across all counties and a 9 percent reduction in homicides when only large counties (populations of 100,000 or more) were included.43
====
====http://johnrlott.tripod.com/Plassmann_Whitley.pdf
COMMENTS
Confirming ìMore Guns, Less Crimeî Florenz Plassmann* & John Whitley**
CONCLUSION Analyzing county-level data for the entire United States from 1977 to 2000, we find annual reductions in murder rates between 1.5% and 2.3% for each additional year that a right-to-carry law is in effect.
For the first five years that such a law is in effect, the total benefit from reduced crimes usually ranges between about $2 and $3 billion per year.
The results are very similar to earlier estimates using county-level data from 1977 to 1996. We appreciate the continuing effort that Ayres and Donohue have made in discussing the impact of right-to-carry laws on crime rates. Yet we believe that both the new evidence provided by them as well as our new results show consistently that right-to-carry laws reduce crime and save lives. Unfortunately, a few simple mistakes lead Ayres and Donohue to incorrectly claim that crime rates significantly increase after right-to-carry laws are initially adopted and to misinterpret the significance of their own estimates that examined the year-to-year impact of the law.
http://crimeresearch.org/wp-content...An-Exercise-in-Replication.proof_.revised.pdf
~ The Impact of Right-to-Carry Laws on Crime: An Exercise in Replication1
Carlisle E. Moody College of William and Mary - Department of Economics, Virginia 23187, U.S.A. E-mail: [email protected] Thomas B. Marvell Justec Research, Virginia 23185, U.S.A. Paul R. Zimmerman U.S. Federal Trade Commission - Bureau of Economics, Washington, D.C., U.S.A. Fasil Alemante College of William and Mary, Virginia 23187, U.S.A.
Abstract: In an article published in 2011, Aneja, Donohue and Zhang found that shall-issue or right-to-carry (RTC) concealed weapons laws have no effect on any crime except for a positive effect on assault.
This paper reports a replication of their basic findings and some corresponding robustness checks, which reveal a serious omitted variable problem.
Once corrected for omitted variables, the most robust result, confirmed using both county and state data, is that RTC laws significantly reduce murder.
====
===An examination of the effects of concealed weapons laws and assault weapons bans on state-level murder rates
Mark Gius
Abstract
The purpose of the present study is to determine the effects of state-level assault weapons bans and concealed weapons laws on state-level murder rates.
Using data for the period 1980 to 2009 and controlling for state and year fixed effects, the results of the present study suggest that states with restrictions on the carrying of concealed weapons had higher gun-related murder rates than other states.
It was also found that assault weapons bans did not significantly affect murder rates at the state level. These results suggest that restrictive concealed weapons laws may cause an increase in gun-related murders at the state level. The results of this study are consistent with some prior research in this area, most notably Lott and Mustard (1997).
“The Debate on Shall-Issue Laws” by Carlisle e. Moody and Thomas B. Marvell, published in Econ Journal Watch, volume 5, number 3, September 2008 It is also available here..
Summary and Conclusion
Many articles have been published finding that shall-issue laws reduce crime. Only one article, by Ayres and Donohue who employ a model that combines a dummy variable with a post-law trend, claims to find that shall-issue laws increase crime.
However, the only way that they can produce the result that shall-issue laws increase crime is to confine the span of analysis to five years
. We show, using their own estimates, that if they had extended their analysis by one more year, they would have concluded that these laws reduce crime.
Since most states with shallissue laws have had these laws on the books for more than five years, and the law will presumably remain on the books for some time, the only relevant analysis extends beyond five years. We extend their analysis by adding three more years of data, control for the effects of crack cocaine, control for dynamic effects, and correct the standard errors for clustering.
We find that there is an initial increase in crime due to passage of the shall-issue law that is dwarfed over time by the decrease in crime associated with the post-law trend.
These results are very similar to those of Ayres and Donohue, properly interpreted.
The modified Ayres and Donohue model finds that shall-issue laws significantly reduce murder and burglary across all the adopting states. These laws appear to significantly increase assault, and have no net effect on rape, robbery, larceny, or auto theft. However, in the long run only the trend coefficients matter. We estimate a net benefit of $450 million per year as a result of the passage of these laws. We also estimate that, up through 2000, there was a cumulative overall net benefit of these laws of $28 billion since their passage. We think that there is credible statistical evidence that these laws lower the costs of crime. But at the very least, the present study should neutralize any “more guns, more crime” thinking based on Ayres and Donohue’s work in the Stanford Law Review
Taking apart ayre and donahue one....
“The Debate on Shall-Issue Laws” by Carlisle e. Moody and Thomas B. Marvell, published in Econ Journal Watch, volume 5, number 3, September 2008 It is also available here..
Abstract
“Shall-issue” laws require authorities to issue concealed-weapons permits to anyone who applies, unless the applicant has a criminal record or a history of mental illness. A large number of studies indicate that shall-issue laws reduce crime. Only one study, an influential paper in the Stanford Law Review (2003) by Ian Ayres and John J. Donohue iii, implies that these laws lead to an increase in crime. We apply an improved version of the Ayres and Donohue method to a more extensive data set. Our analysis, as well as Ayres and Donohue’s when projected beyond a five-year span, indicates that shall-issue laws decrease crime and the costs of crime. Purists in statistical analysis object with some cause to some of methods employed both by Ayres and Donohue and by us. But our paper upgrades Ayres and Donohue, so, until the next study comes along, our paper should neutralize Ayres and Donohue’s “more guns, more crime” conclusion.
Summary and Conclusion Many articles have been published finding that shall-issue laws reduce crime. Only one article, by Ayres and Donohue who employ a model that combines a dummy variable with a post-law trend, claims to find that shall-issue laws increase crime. However, the only way that they can produce the result that shall-issue laws increase crime is to confine the span of analysis to five years. We show, using their own estimates, that if they had extended their analysis by one more year, they would have concluded that these laws reduce crime. Since most states with shallissue laws have had these laws on the books for more than five years, and the law will presumably remain on the books for some time, the only relevant analysis extends beyond five years. We extend their analysis by adding three more years of data, control for the effects of crack cocaine, control for dynamic effects, and correct the standard errors for clustering. We find that there is an initial increase in crime due to passage of the shall-issue law that is dwarfed over time by the decrease in crime associated with the post-law trend. These results are very similar to those of Ayres and Donohue, properly interpreted. The modified Ayres and Donohue model finds that shall-issue laws significantly reduce murder and burglary across all the adopting states. These laws appear to significantly increase assault, and have no net effect on rape, robbery, larceny, or auto theft. However, in the long run only the trend coefficients matter.
We estimate a net benefit of $450 million per year as a result of the passage of these laws.
We also estimate that, up through 2000, there was a cumulative overall net benefit of these laws of $28 billion since their passage.
We think that there is credible statistical evidence that these laws lower the costs of crime. But at the very least, the present study should neutralize any “more guns, more crime” thinking based on Ayres and Donohue’s work in the Stanford Law Review. We acknowledge that, especially in light of the methodological issues of the literature in general, the magnitudes derived from our analysis of crime statistics and the supposed costs of crime might be dwarfed by other considerations in judging the policy issue. Some might contend that allowing individuals to carry a concealed weapon is a moral or cultural bad. Others might contend that greater liberty is a moral or cultural good. All we are confident in saying is that the evidence, such as it is, seems to support the hypothesis that the shall-issue law is generally beneficial with respect to its overall long run effect on crime.
No...it doesn't.....it tries to link concealed carry to mass public shootings and I showed you how even the simplest question debunks the entire study on that point........
The study you found claims concealed carry gun permit numbers increase mass public shootings....I showed you that this is stupid and dumb as a claim...
You can't explain the link either...
Mass public shooters don't need a concealed carry permit to carry the gun to the place where they plan on committing mass murder.......
Criminals who can't legally buy, own or carry guns, can't get a legal carry permit to carry their already illegal gun.......and they are the ones committing almost all of the murder in this country in democrat party controlled cities...
Your study is crap.......
What the article says is that looser concealed carry laws contribute to more gun deaths in general - not just mass shootings. As a separate point, it says the good guy with a gun idea doesn’t affect mass shootings.Okay again , the violent crime rates across the board have been going down. My study specifically makes the connection between gun ownership and GUN DEATHS SPECIFICALLY. Your so called studies are simply looking at crime trends that have already been going down anyway.A lot of things can be bi-directional. Studies suggest this for this reason. You have no good reason to actually believe that shit. Your confidence is based on nothing. Either way, nothing good comes from more higher gun ownership. Clearly people owning more guns doesn’t stop the crime rate anyway. The result is more bad people with guns.No, it isn't as the article clearly states and I have shown. Increased gun ownership is far more likely to be a result of violent crime than the cause. I doubt you even bothered to read what you linked to and have no idea what it says. That's why I quoted it. But apparently you didn't bother to read that either.It’s linked in the article idiot.SHOW ME THE FUCKING RESEARCH OR FUCK OFF, YAHOO "NEWS"!!!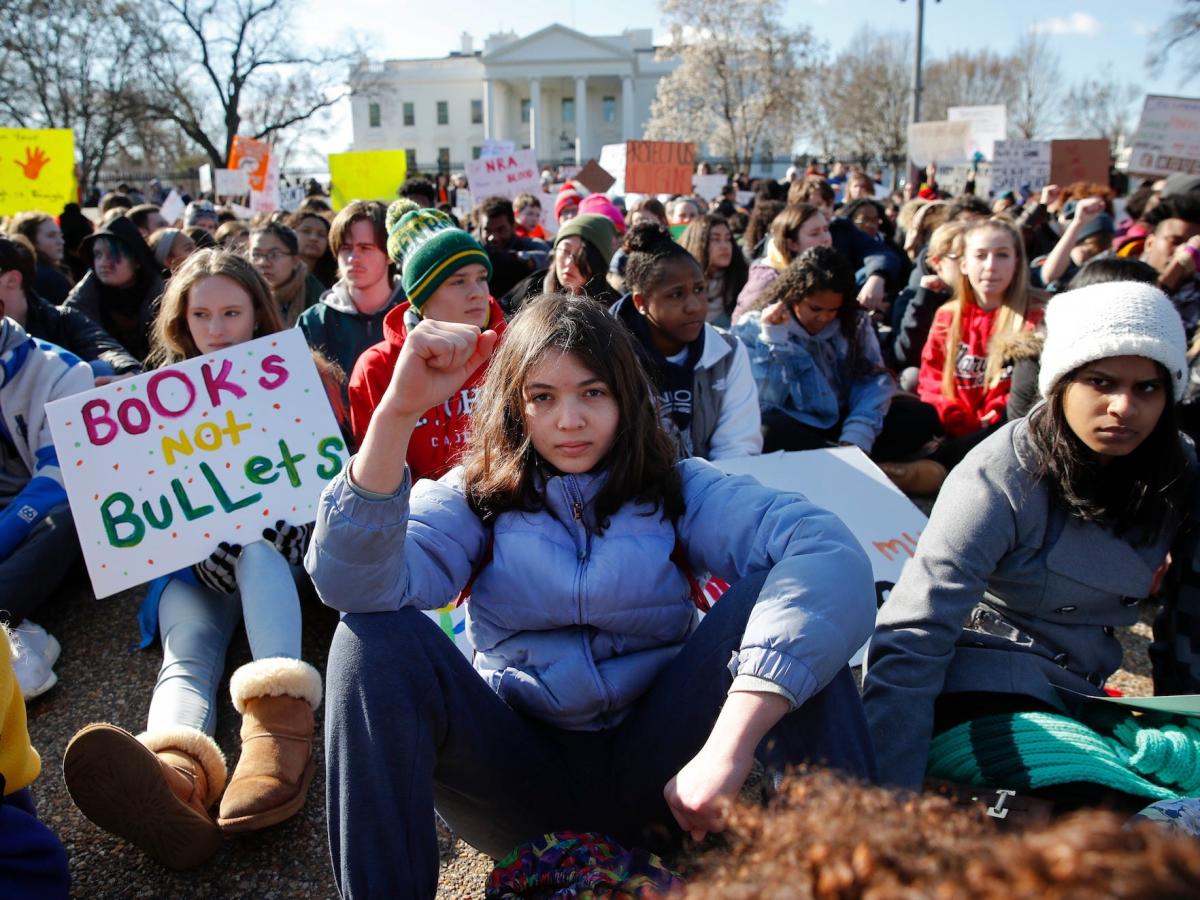
New research puts the 'good guy with a gun' idea to rest: Loose concealed-carry laws are linked to more firearm homicides
States with looser concealed-carry laws have higher rates of gun homicide. And higher gun-ownership rates are associated with more mass shootings.www.yahoo.com
A new study found that states with looser concealed-carry gun laws have higher rates of gun homicide.
The results also showed that higher levels of gun ownership are associated with more mass shootings.
The study suggests the US could reduce gun violence by lowering levels of gun ownership and passing stricter concealed-carry laws.
Visit Business Insider's homepage for more stories.
The "good guy with a gun" theory goes like this: If more well-intentioned people carry guns, there's a higher chance of stopping a violent shooter.
Unfortunately, that's not how it works in real life, according to new research published in the journal Justice Quarterly. The study found that laws allowing more people to carry guns in public are associated with a rise in gun violence. The results also showed that the higher a state's gun-ownership rate, the more likely a mass shooting is.
Here...actual research proving you wrong...
Right-to-Carry Concealed Weapon Laws and Homicide in Large U.S. Counties: The Effect on Weapon Types, Victim Characteristics, and Victim-Offender Relationships By DAVID E. OLSON AND MICHAEL D. MALTZ, Journal of Law and Economics, October 2001
Our results indicated that the direction of effect of the shall-issue law on total SHR homicide rates was similar to that obtained by Lott and Mustard, although the magnitude of the effect was somewhat smaller and was statistically significant at the 7 percent level. In our analysis, which included only counties with a 1977 population of 100,000 or more, laws allowing for concealed weapons were associated with a 6.52 percent reduction in total homicides (Table 2). By comparison, Lott and Mustard found the concealed weapon dummy variable to be associated with a 7.65 percent reduction in total homicides across all counties and a 9 percent reduction in homicides when only large counties (populations of 100,000 or more) were included.43
====
====http://johnrlott.tripod.com/Plassmann_Whitley.pdf
COMMENTS
Confirming ìMore Guns, Less Crimeî Florenz Plassmann* & John Whitley**
CONCLUSION Analyzing county-level data for the entire United States from 1977 to 2000, we find annual reductions in murder rates between 1.5% and 2.3% for each additional year that a right-to-carry law is in effect.
For the first five years that such a law is in effect, the total benefit from reduced crimes usually ranges between about $2 and $3 billion per year.
The results are very similar to earlier estimates using county-level data from 1977 to 1996. We appreciate the continuing effort that Ayres and Donohue have made in discussing the impact of right-to-carry laws on crime rates. Yet we believe that both the new evidence provided by them as well as our new results show consistently that right-to-carry laws reduce crime and save lives. Unfortunately, a few simple mistakes lead Ayres and Donohue to incorrectly claim that crime rates significantly increase after right-to-carry laws are initially adopted and to misinterpret the significance of their own estimates that examined the year-to-year impact of the law.
http://crimeresearch.org/wp-content...An-Exercise-in-Replication.proof_.revised.pdf
~ The Impact of Right-to-Carry Laws on Crime: An Exercise in Replication1
Carlisle E. Moody College of William and Mary - Department of Economics, Virginia 23187, U.S.A. E-mail: [email protected] Thomas B. Marvell Justec Research, Virginia 23185, U.S.A. Paul R. Zimmerman U.S. Federal Trade Commission - Bureau of Economics, Washington, D.C., U.S.A. Fasil Alemante College of William and Mary, Virginia 23187, U.S.A.
Abstract: In an article published in 2011, Aneja, Donohue and Zhang found that shall-issue or right-to-carry (RTC) concealed weapons laws have no effect on any crime except for a positive effect on assault.
This paper reports a replication of their basic findings and some corresponding robustness checks, which reveal a serious omitted variable problem.
Once corrected for omitted variables, the most robust result, confirmed using both county and state data, is that RTC laws significantly reduce murder.
====
===An examination of the effects of concealed weapons laws and assault weapons bans on state-level murder rates
Mark Gius
Abstract
The purpose of the present study is to determine the effects of state-level assault weapons bans and concealed weapons laws on state-level murder rates.
Using data for the period 1980 to 2009 and controlling for state and year fixed effects, the results of the present study suggest that states with restrictions on the carrying of concealed weapons had higher gun-related murder rates than other states.
It was also found that assault weapons bans did not significantly affect murder rates at the state level. These results suggest that restrictive concealed weapons laws may cause an increase in gun-related murders at the state level. The results of this study are consistent with some prior research in this area, most notably Lott and Mustard (1997).
“The Debate on Shall-Issue Laws” by Carlisle e. Moody and Thomas B. Marvell, published in Econ Journal Watch, volume 5, number 3, September 2008 It is also available here..
Summary and Conclusion
Many articles have been published finding that shall-issue laws reduce crime. Only one article, by Ayres and Donohue who employ a model that combines a dummy variable with a post-law trend, claims to find that shall-issue laws increase crime.
However, the only way that they can produce the result that shall-issue laws increase crime is to confine the span of analysis to five years
. We show, using their own estimates, that if they had extended their analysis by one more year, they would have concluded that these laws reduce crime.
Since most states with shallissue laws have had these laws on the books for more than five years, and the law will presumably remain on the books for some time, the only relevant analysis extends beyond five years. We extend their analysis by adding three more years of data, control for the effects of crack cocaine, control for dynamic effects, and correct the standard errors for clustering.
We find that there is an initial increase in crime due to passage of the shall-issue law that is dwarfed over time by the decrease in crime associated with the post-law trend.
These results are very similar to those of Ayres and Donohue, properly interpreted.
The modified Ayres and Donohue model finds that shall-issue laws significantly reduce murder and burglary across all the adopting states. These laws appear to significantly increase assault, and have no net effect on rape, robbery, larceny, or auto theft. However, in the long run only the trend coefficients matter. We estimate a net benefit of $450 million per year as a result of the passage of these laws. We also estimate that, up through 2000, there was a cumulative overall net benefit of these laws of $28 billion since their passage. We think that there is credible statistical evidence that these laws lower the costs of crime. But at the very least, the present study should neutralize any “more guns, more crime” thinking based on Ayres and Donohue’s work in the Stanford Law Review
Taking apart ayre and donahue one....
“The Debate on Shall-Issue Laws” by Carlisle e. Moody and Thomas B. Marvell, published in Econ Journal Watch, volume 5, number 3, September 2008 It is also available here..
Abstract
“Shall-issue” laws require authorities to issue concealed-weapons permits to anyone who applies, unless the applicant has a criminal record or a history of mental illness. A large number of studies indicate that shall-issue laws reduce crime. Only one study, an influential paper in the Stanford Law Review (2003) by Ian Ayres and John J. Donohue iii, implies that these laws lead to an increase in crime. We apply an improved version of the Ayres and Donohue method to a more extensive data set. Our analysis, as well as Ayres and Donohue’s when projected beyond a five-year span, indicates that shall-issue laws decrease crime and the costs of crime. Purists in statistical analysis object with some cause to some of methods employed both by Ayres and Donohue and by us. But our paper upgrades Ayres and Donohue, so, until the next study comes along, our paper should neutralize Ayres and Donohue’s “more guns, more crime” conclusion.
Summary and Conclusion Many articles have been published finding that shall-issue laws reduce crime. Only one article, by Ayres and Donohue who employ a model that combines a dummy variable with a post-law trend, claims to find that shall-issue laws increase crime. However, the only way that they can produce the result that shall-issue laws increase crime is to confine the span of analysis to five years. We show, using their own estimates, that if they had extended their analysis by one more year, they would have concluded that these laws reduce crime. Since most states with shallissue laws have had these laws on the books for more than five years, and the law will presumably remain on the books for some time, the only relevant analysis extends beyond five years. We extend their analysis by adding three more years of data, control for the effects of crack cocaine, control for dynamic effects, and correct the standard errors for clustering. We find that there is an initial increase in crime due to passage of the shall-issue law that is dwarfed over time by the decrease in crime associated with the post-law trend. These results are very similar to those of Ayres and Donohue, properly interpreted. The modified Ayres and Donohue model finds that shall-issue laws significantly reduce murder and burglary across all the adopting states. These laws appear to significantly increase assault, and have no net effect on rape, robbery, larceny, or auto theft. However, in the long run only the trend coefficients matter.
We estimate a net benefit of $450 million per year as a result of the passage of these laws.
We also estimate that, up through 2000, there was a cumulative overall net benefit of these laws of $28 billion since their passage.
We think that there is credible statistical evidence that these laws lower the costs of crime. But at the very least, the present study should neutralize any “more guns, more crime” thinking based on Ayres and Donohue’s work in the Stanford Law Review. We acknowledge that, especially in light of the methodological issues of the literature in general, the magnitudes derived from our analysis of crime statistics and the supposed costs of crime might be dwarfed by other considerations in judging the policy issue. Some might contend that allowing individuals to carry a concealed weapon is a moral or cultural bad. Others might contend that greater liberty is a moral or cultural good. All we are confident in saying is that the evidence, such as it is, seems to support the hypothesis that the shall-issue law is generally beneficial with respect to its overall long run effect on crime.
No...it doesn't.....it tries to link concealed carry to mass public shootings and I showed you how even the simplest question debunks the entire study on that point........
The study you found claims concealed carry gun permit numbers increase mass public shootings....I showed you that this is stupid and dumb as a claim...
You can't explain the link either...
Mass public shooters don't need a concealed carry permit to carry the gun to the place where they plan on committing mass murder.......
Criminals who can't legally buy, own or carry guns, can't get a legal carry permit to carry their already illegal gun.......and they are the ones committing almost all of the murder in this country in democrat party controlled cities...
Your study is crap.......
Lol how about you explain HOW concealed carry helps to reduce crime rates? What sense does that make? Perhaps if you said open carry I would believe you.What the article says is that looser concealed carry laws contribute to more gun deaths in general - not just mass shootings. As a separate point, it says the good guy with a gun idea doesn’t affect mass shootings.Okay again , the violent crime rates across the board have been going down. My study specifically makes the connection between gun ownership and GUN DEATHS SPECIFICALLY. Your so called studies are simply looking at crime trends that have already been going down anyway.A lot of things can be bi-directional. Studies suggest this for this reason. You have no good reason to actually believe that shit. Your confidence is based on nothing. Either way, nothing good comes from more higher gun ownership. Clearly people owning more guns doesn’t stop the crime rate anyway. The result is more bad people with guns.No, it isn't as the article clearly states and I have shown. Increased gun ownership is far more likely to be a result of violent crime than the cause. I doubt you even bothered to read what you linked to and have no idea what it says. That's why I quoted it. But apparently you didn't bother to read that either.It’s linked in the article idiot.SHOW ME THE FUCKING RESEARCH OR FUCK OFF, YAHOO "NEWS"!!!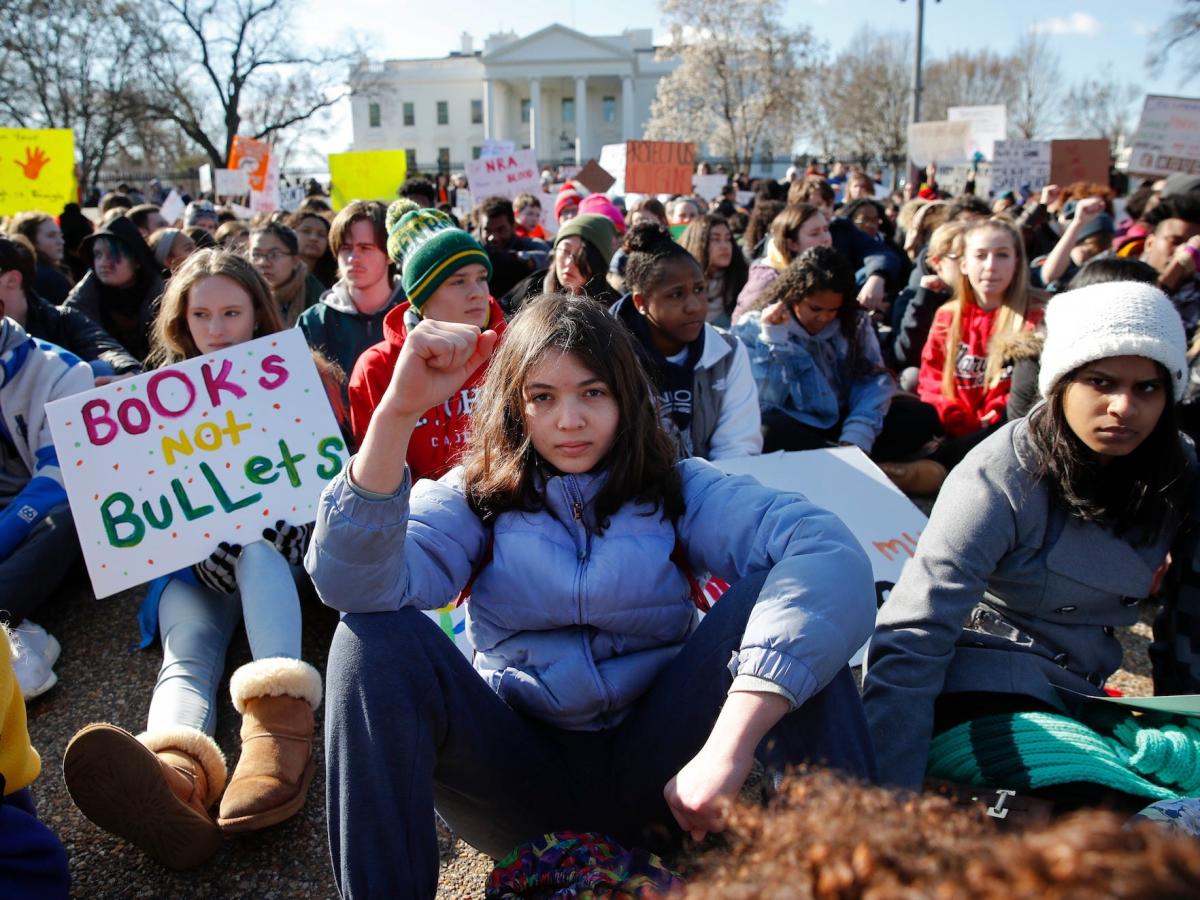
New research puts the 'good guy with a gun' idea to rest: Loose concealed-carry laws are linked to more firearm homicides
States with looser concealed-carry laws have higher rates of gun homicide. And higher gun-ownership rates are associated with more mass shootings.www.yahoo.com
A new study found that states with looser concealed-carry gun laws have higher rates of gun homicide.
The results also showed that higher levels of gun ownership are associated with more mass shootings.
The study suggests the US could reduce gun violence by lowering levels of gun ownership and passing stricter concealed-carry laws.
Visit Business Insider's homepage for more stories.
The "good guy with a gun" theory goes like this: If more well-intentioned people carry guns, there's a higher chance of stopping a violent shooter.
Unfortunately, that's not how it works in real life, according to new research published in the journal Justice Quarterly. The study found that laws allowing more people to carry guns in public are associated with a rise in gun violence. The results also showed that the higher a state's gun-ownership rate, the more likely a mass shooting is.
Here...actual research proving you wrong...
Right-to-Carry Concealed Weapon Laws and Homicide in Large U.S. Counties: The Effect on Weapon Types, Victim Characteristics, and Victim-Offender Relationships By DAVID E. OLSON AND MICHAEL D. MALTZ, Journal of Law and Economics, October 2001
Our results indicated that the direction of effect of the shall-issue law on total SHR homicide rates was similar to that obtained by Lott and Mustard, although the magnitude of the effect was somewhat smaller and was statistically significant at the 7 percent level. In our analysis, which included only counties with a 1977 population of 100,000 or more, laws allowing for concealed weapons were associated with a 6.52 percent reduction in total homicides (Table 2). By comparison, Lott and Mustard found the concealed weapon dummy variable to be associated with a 7.65 percent reduction in total homicides across all counties and a 9 percent reduction in homicides when only large counties (populations of 100,000 or more) were included.43
====
====http://johnrlott.tripod.com/Plassmann_Whitley.pdf
COMMENTS
Confirming ìMore Guns, Less Crimeî Florenz Plassmann* & John Whitley**
CONCLUSION Analyzing county-level data for the entire United States from 1977 to 2000, we find annual reductions in murder rates between 1.5% and 2.3% for each additional year that a right-to-carry law is in effect.
For the first five years that such a law is in effect, the total benefit from reduced crimes usually ranges between about $2 and $3 billion per year.
The results are very similar to earlier estimates using county-level data from 1977 to 1996. We appreciate the continuing effort that Ayres and Donohue have made in discussing the impact of right-to-carry laws on crime rates. Yet we believe that both the new evidence provided by them as well as our new results show consistently that right-to-carry laws reduce crime and save lives. Unfortunately, a few simple mistakes lead Ayres and Donohue to incorrectly claim that crime rates significantly increase after right-to-carry laws are initially adopted and to misinterpret the significance of their own estimates that examined the year-to-year impact of the law.
http://crimeresearch.org/wp-content...An-Exercise-in-Replication.proof_.revised.pdf
~ The Impact of Right-to-Carry Laws on Crime: An Exercise in Replication1
Carlisle E. Moody College of William and Mary - Department of Economics, Virginia 23187, U.S.A. E-mail: [email protected] Thomas B. Marvell Justec Research, Virginia 23185, U.S.A. Paul R. Zimmerman U.S. Federal Trade Commission - Bureau of Economics, Washington, D.C., U.S.A. Fasil Alemante College of William and Mary, Virginia 23187, U.S.A.
Abstract: In an article published in 2011, Aneja, Donohue and Zhang found that shall-issue or right-to-carry (RTC) concealed weapons laws have no effect on any crime except for a positive effect on assault.
This paper reports a replication of their basic findings and some corresponding robustness checks, which reveal a serious omitted variable problem.
Once corrected for omitted variables, the most robust result, confirmed using both county and state data, is that RTC laws significantly reduce murder.
====
===An examination of the effects of concealed weapons laws and assault weapons bans on state-level murder rates
Mark Gius
Abstract
The purpose of the present study is to determine the effects of state-level assault weapons bans and concealed weapons laws on state-level murder rates.
Using data for the period 1980 to 2009 and controlling for state and year fixed effects, the results of the present study suggest that states with restrictions on the carrying of concealed weapons had higher gun-related murder rates than other states.
It was also found that assault weapons bans did not significantly affect murder rates at the state level. These results suggest that restrictive concealed weapons laws may cause an increase in gun-related murders at the state level. The results of this study are consistent with some prior research in this area, most notably Lott and Mustard (1997).
“The Debate on Shall-Issue Laws” by Carlisle e. Moody and Thomas B. Marvell, published in Econ Journal Watch, volume 5, number 3, September 2008 It is also available here..
Summary and Conclusion
Many articles have been published finding that shall-issue laws reduce crime. Only one article, by Ayres and Donohue who employ a model that combines a dummy variable with a post-law trend, claims to find that shall-issue laws increase crime.
However, the only way that they can produce the result that shall-issue laws increase crime is to confine the span of analysis to five years
. We show, using their own estimates, that if they had extended their analysis by one more year, they would have concluded that these laws reduce crime.
Since most states with shallissue laws have had these laws on the books for more than five years, and the law will presumably remain on the books for some time, the only relevant analysis extends beyond five years. We extend their analysis by adding three more years of data, control for the effects of crack cocaine, control for dynamic effects, and correct the standard errors for clustering.
We find that there is an initial increase in crime due to passage of the shall-issue law that is dwarfed over time by the decrease in crime associated with the post-law trend.
These results are very similar to those of Ayres and Donohue, properly interpreted.
The modified Ayres and Donohue model finds that shall-issue laws significantly reduce murder and burglary across all the adopting states. These laws appear to significantly increase assault, and have no net effect on rape, robbery, larceny, or auto theft. However, in the long run only the trend coefficients matter. We estimate a net benefit of $450 million per year as a result of the passage of these laws. We also estimate that, up through 2000, there was a cumulative overall net benefit of these laws of $28 billion since their passage. We think that there is credible statistical evidence that these laws lower the costs of crime. But at the very least, the present study should neutralize any “more guns, more crime” thinking based on Ayres and Donohue’s work in the Stanford Law Review
Taking apart ayre and donahue one....
“The Debate on Shall-Issue Laws” by Carlisle e. Moody and Thomas B. Marvell, published in Econ Journal Watch, volume 5, number 3, September 2008 It is also available here..
Abstract
“Shall-issue” laws require authorities to issue concealed-weapons permits to anyone who applies, unless the applicant has a criminal record or a history of mental illness. A large number of studies indicate that shall-issue laws reduce crime. Only one study, an influential paper in the Stanford Law Review (2003) by Ian Ayres and John J. Donohue iii, implies that these laws lead to an increase in crime. We apply an improved version of the Ayres and Donohue method to a more extensive data set. Our analysis, as well as Ayres and Donohue’s when projected beyond a five-year span, indicates that shall-issue laws decrease crime and the costs of crime. Purists in statistical analysis object with some cause to some of methods employed both by Ayres and Donohue and by us. But our paper upgrades Ayres and Donohue, so, until the next study comes along, our paper should neutralize Ayres and Donohue’s “more guns, more crime” conclusion.
Summary and Conclusion Many articles have been published finding that shall-issue laws reduce crime. Only one article, by Ayres and Donohue who employ a model that combines a dummy variable with a post-law trend, claims to find that shall-issue laws increase crime. However, the only way that they can produce the result that shall-issue laws increase crime is to confine the span of analysis to five years. We show, using their own estimates, that if they had extended their analysis by one more year, they would have concluded that these laws reduce crime. Since most states with shallissue laws have had these laws on the books for more than five years, and the law will presumably remain on the books for some time, the only relevant analysis extends beyond five years. We extend their analysis by adding three more years of data, control for the effects of crack cocaine, control for dynamic effects, and correct the standard errors for clustering. We find that there is an initial increase in crime due to passage of the shall-issue law that is dwarfed over time by the decrease in crime associated with the post-law trend. These results are very similar to those of Ayres and Donohue, properly interpreted. The modified Ayres and Donohue model finds that shall-issue laws significantly reduce murder and burglary across all the adopting states. These laws appear to significantly increase assault, and have no net effect on rape, robbery, larceny, or auto theft. However, in the long run only the trend coefficients matter.
We estimate a net benefit of $450 million per year as a result of the passage of these laws.
We also estimate that, up through 2000, there was a cumulative overall net benefit of these laws of $28 billion since their passage.
We think that there is credible statistical evidence that these laws lower the costs of crime. But at the very least, the present study should neutralize any “more guns, more crime” thinking based on Ayres and Donohue’s work in the Stanford Law Review. We acknowledge that, especially in light of the methodological issues of the literature in general, the magnitudes derived from our analysis of crime statistics and the supposed costs of crime might be dwarfed by other considerations in judging the policy issue. Some might contend that allowing individuals to carry a concealed weapon is a moral or cultural bad. Others might contend that greater liberty is a moral or cultural good. All we are confident in saying is that the evidence, such as it is, seems to support the hypothesis that the shall-issue law is generally beneficial with respect to its overall long run effect on crime.
No...it doesn't.....it tries to link concealed carry to mass public shootings and I showed you how even the simplest question debunks the entire study on that point........
The study you found claims concealed carry gun permit numbers increase mass public shootings....I showed you that this is stupid and dumb as a claim...
You can't explain the link either...
Mass public shooters don't need a concealed carry permit to carry the gun to the place where they plan on committing mass murder.......
Criminals who can't legally buy, own or carry guns, can't get a legal carry permit to carry their already illegal gun.......and they are the ones committing almost all of the murder in this country in democrat party controlled cities...
Your study is crap.......
It can't prove that since making a connection between law abiding permit holders makes no sense...since the majority of all crime and gun murder is committed by people who can't legally have a gun permit for their already illegal guns.........
And I just posted other real studies showing that concealed carry, in fact, helps to reduce the crime rate......
As has already been explained to you, the vast majority of mass shootings occur where it's illegal to carry a firearm.Again, the point is, moron, that the vast majority of mass shootings ARE NOT prevented by a good guy with a gun. That’s the only point that matters.Lol this study is cherry picking instances where a good guy with a gun happened - a grand total of 25 times lol. Why this doesn’t matter is because the large majority of mass shootings did NOT have a good guy with a gun.
New research puts the 'good guy with a gun' idea to rest: Loose concealed-carry laws are linked to more firearm homicides
States with looser concealed-carry laws have higher rates of gun homicide. And higher gun-ownership rates are associated with more mass shootings.www.yahoo.com
A new study found that states with looser concealed-carry gun laws have higher rates of gun homicide.
The results also showed that higher levels of gun ownership are associated with more mass shootings.
The study suggests the US could reduce gun violence by lowering levels of gun ownership and passing stricter concealed-carry laws.
Visit Business Insider's homepage for more stories.
The "good guy with a gun" theory goes like this: If more well-intentioned people carry guns, there's a higher chance of stopping a violent shooter.
Unfortunately, that's not how it works in real life, according to new research published in the journal Justice Quarterly. The study found that laws allowing more people to carry guns in public are associated with a rise in gun violence. The results also showed that the higher a state's gun-ownership rate, the more likely a mass shooting is.
Here...some actual truth....
Armed Citizens Are Successful 94% Of The Time At Active Shooter Events [FBI]
Of all the active shooter events there were 33 at which an armed citizen was present. Of those, Armed Citizens were successful at stopping the Active shooter 75.8% of the time (25 incidents) and were successful in reducing the loss of life in an additional 18.2% (6) of incidents. In only 2 of the 33 incidents (6.1%) was the Armed Citizen(s) not helpful in any way in stopping the active shooter or reducing the loss of life.
Thus the headline of our report that Armed Citizens Are Successful 94% Of The Time At Active Shooter Events.
In the 2 incidents at which the armed citizen “failed” to stop or slow the active shooter, one is the previously mentioned incident with hunters. The other is an incident in which the CCWer was shot in the back in a Las Vegas Walmart when he failed to identify that there were 2 Active Shooters involved in the attack. He neglected to identify the one that shot him in the back while he was trying to ambush the other perpetrator.
We also decided to look at the breakdown of events that took place in gun free zones and the relative death toll from events in gun free zones vs non-gun-free zones.
Of the 283 incidents in our data pool, we were unable to identify if the event took place in a gun-free zone in a large number (41%) of the events. Most of the events took place at a business, church, home, or other places at which as a rule of law it is not a gun free zone but potentially could have been declared one by the property owner. Without any information in the FBI study or any indication one way or the other from the news reports, we have indicated that event with a question mark.
If you look at all of the Active Shooter events (pie chart on the top) you see that for those which we have the information, almost twice as many took place in gun free zones than not; but realistically the vast majority of those for which we have no information (indicated as ?) are probably NOT gun free zones.
If you isolate just the events at which 8 or more people were killed the data paints a different picture (pie chart on the bottom). In these incidents, 77.8% took place in a gun-free zone suggesting that gun free zones lead to a higher death rate vs active shooter events in general
=====
One of the final metrics we thought was important to consider is the potential tendency for armed citizens to injure or kill innocent people in their attempt to “save the day.” A common point in political discussions is to point out the lack of training of most armed citizens and the decrease in safety inherent in their presence during violent encounters.
As you can see below, however, at the 33 incidents at which Armed Citizens were present, there were zero situations at which the Armed Citizen injured or killed an innocent person. It never happened.
Moron....those are mass public shootings where the good guys had guns.....versus the over 90% of the locations that are gun free zones...you moron.......
When you make almosts every public space a gun free zone, normal, law abiding people will not break the law and carry their guns....so these are mass public shootings that took place in locations where someone had their gun on them......you dumb shit........
You don't know what you are talking about.
It's quite simple, dumbass: thugs don't want to assault people who might be armed. They don't want to break-in to houses where the residents might be armed.Lol how about you explain HOW concealed carry helps to reduce crime rates? What sense does that make? Perhaps if you said open carry I would believe you.What the article says is that looser concealed carry laws contribute to more gun deaths in general - not just mass shootings. As a separate point, it says the good guy with a gun idea doesn’t affect mass shootings.Okay again , the violent crime rates across the board have been going down. My study specifically makes the connection between gun ownership and GUN DEATHS SPECIFICALLY. Your so called studies are simply looking at crime trends that have already been going down anyway.A lot of things can be bi-directional. Studies suggest this for this reason. You have no good reason to actually believe that shit. Your confidence is based on nothing. Either way, nothing good comes from more higher gun ownership. Clearly people owning more guns doesn’t stop the crime rate anyway. The result is more bad people with guns.No, it isn't as the article clearly states and I have shown. Increased gun ownership is far more likely to be a result of violent crime than the cause. I doubt you even bothered to read what you linked to and have no idea what it says. That's why I quoted it. But apparently you didn't bother to read that either.It’s linked in the article idiot.SHOW ME THE FUCKING RESEARCH OR FUCK OFF, YAHOO "NEWS"!!!
New research puts the 'good guy with a gun' idea to rest: Loose concealed-carry laws are linked to more firearm homicides
States with looser concealed-carry laws have higher rates of gun homicide. And higher gun-ownership rates are associated with more mass shootings.www.yahoo.com
A new study found that states with looser concealed-carry gun laws have higher rates of gun homicide.
The results also showed that higher levels of gun ownership are associated with more mass shootings.
The study suggests the US could reduce gun violence by lowering levels of gun ownership and passing stricter concealed-carry laws.
Visit Business Insider's homepage for more stories.
The "good guy with a gun" theory goes like this: If more well-intentioned people carry guns, there's a higher chance of stopping a violent shooter.
Unfortunately, that's not how it works in real life, according to new research published in the journal Justice Quarterly. The study found that laws allowing more people to carry guns in public are associated with a rise in gun violence. The results also showed that the higher a state's gun-ownership rate, the more likely a mass shooting is.
Here...actual research proving you wrong...
Right-to-Carry Concealed Weapon Laws and Homicide in Large U.S. Counties: The Effect on Weapon Types, Victim Characteristics, and Victim-Offender Relationships By DAVID E. OLSON AND MICHAEL D. MALTZ, Journal of Law and Economics, October 2001
Our results indicated that the direction of effect of the shall-issue law on total SHR homicide rates was similar to that obtained by Lott and Mustard, although the magnitude of the effect was somewhat smaller and was statistically significant at the 7 percent level. In our analysis, which included only counties with a 1977 population of 100,000 or more, laws allowing for concealed weapons were associated with a 6.52 percent reduction in total homicides (Table 2). By comparison, Lott and Mustard found the concealed weapon dummy variable to be associated with a 7.65 percent reduction in total homicides across all counties and a 9 percent reduction in homicides when only large counties (populations of 100,000 or more) were included.43
====
====http://johnrlott.tripod.com/Plassmann_Whitley.pdf
COMMENTS
Confirming ìMore Guns, Less Crimeî Florenz Plassmann* & John Whitley**
CONCLUSION Analyzing county-level data for the entire United States from 1977 to 2000, we find annual reductions in murder rates between 1.5% and 2.3% for each additional year that a right-to-carry law is in effect.
For the first five years that such a law is in effect, the total benefit from reduced crimes usually ranges between about $2 and $3 billion per year.
The results are very similar to earlier estimates using county-level data from 1977 to 1996. We appreciate the continuing effort that Ayres and Donohue have made in discussing the impact of right-to-carry laws on crime rates. Yet we believe that both the new evidence provided by them as well as our new results show consistently that right-to-carry laws reduce crime and save lives. Unfortunately, a few simple mistakes lead Ayres and Donohue to incorrectly claim that crime rates significantly increase after right-to-carry laws are initially adopted and to misinterpret the significance of their own estimates that examined the year-to-year impact of the law.
http://crimeresearch.org/wp-content...An-Exercise-in-Replication.proof_.revised.pdf
~ The Impact of Right-to-Carry Laws on Crime: An Exercise in Replication1
Carlisle E. Moody College of William and Mary - Department of Economics, Virginia 23187, U.S.A. E-mail: [email protected] Thomas B. Marvell Justec Research, Virginia 23185, U.S.A. Paul R. Zimmerman U.S. Federal Trade Commission - Bureau of Economics, Washington, D.C., U.S.A. Fasil Alemante College of William and Mary, Virginia 23187, U.S.A.
Abstract: In an article published in 2011, Aneja, Donohue and Zhang found that shall-issue or right-to-carry (RTC) concealed weapons laws have no effect on any crime except for a positive effect on assault.
This paper reports a replication of their basic findings and some corresponding robustness checks, which reveal a serious omitted variable problem.
Once corrected for omitted variables, the most robust result, confirmed using both county and state data, is that RTC laws significantly reduce murder.
====
===An examination of the effects of concealed weapons laws and assault weapons bans on state-level murder rates
Mark Gius
Abstract
The purpose of the present study is to determine the effects of state-level assault weapons bans and concealed weapons laws on state-level murder rates.
Using data for the period 1980 to 2009 and controlling for state and year fixed effects, the results of the present study suggest that states with restrictions on the carrying of concealed weapons had higher gun-related murder rates than other states.
It was also found that assault weapons bans did not significantly affect murder rates at the state level. These results suggest that restrictive concealed weapons laws may cause an increase in gun-related murders at the state level. The results of this study are consistent with some prior research in this area, most notably Lott and Mustard (1997).
“The Debate on Shall-Issue Laws” by Carlisle e. Moody and Thomas B. Marvell, published in Econ Journal Watch, volume 5, number 3, September 2008 It is also available here..
Summary and Conclusion
Many articles have been published finding that shall-issue laws reduce crime. Only one article, by Ayres and Donohue who employ a model that combines a dummy variable with a post-law trend, claims to find that shall-issue laws increase crime.
However, the only way that they can produce the result that shall-issue laws increase crime is to confine the span of analysis to five years
. We show, using their own estimates, that if they had extended their analysis by one more year, they would have concluded that these laws reduce crime.
Since most states with shallissue laws have had these laws on the books for more than five years, and the law will presumably remain on the books for some time, the only relevant analysis extends beyond five years. We extend their analysis by adding three more years of data, control for the effects of crack cocaine, control for dynamic effects, and correct the standard errors for clustering.
We find that there is an initial increase in crime due to passage of the shall-issue law that is dwarfed over time by the decrease in crime associated with the post-law trend.
These results are very similar to those of Ayres and Donohue, properly interpreted.
The modified Ayres and Donohue model finds that shall-issue laws significantly reduce murder and burglary across all the adopting states. These laws appear to significantly increase assault, and have no net effect on rape, robbery, larceny, or auto theft. However, in the long run only the trend coefficients matter. We estimate a net benefit of $450 million per year as a result of the passage of these laws. We also estimate that, up through 2000, there was a cumulative overall net benefit of these laws of $28 billion since their passage. We think that there is credible statistical evidence that these laws lower the costs of crime. But at the very least, the present study should neutralize any “more guns, more crime” thinking based on Ayres and Donohue’s work in the Stanford Law Review
Taking apart ayre and donahue one....
“The Debate on Shall-Issue Laws” by Carlisle e. Moody and Thomas B. Marvell, published in Econ Journal Watch, volume 5, number 3, September 2008 It is also available here..
Abstract
“Shall-issue” laws require authorities to issue concealed-weapons permits to anyone who applies, unless the applicant has a criminal record or a history of mental illness. A large number of studies indicate that shall-issue laws reduce crime. Only one study, an influential paper in the Stanford Law Review (2003) by Ian Ayres and John J. Donohue iii, implies that these laws lead to an increase in crime. We apply an improved version of the Ayres and Donohue method to a more extensive data set. Our analysis, as well as Ayres and Donohue’s when projected beyond a five-year span, indicates that shall-issue laws decrease crime and the costs of crime. Purists in statistical analysis object with some cause to some of methods employed both by Ayres and Donohue and by us. But our paper upgrades Ayres and Donohue, so, until the next study comes along, our paper should neutralize Ayres and Donohue’s “more guns, more crime” conclusion.
Summary and Conclusion Many articles have been published finding that shall-issue laws reduce crime. Only one article, by Ayres and Donohue who employ a model that combines a dummy variable with a post-law trend, claims to find that shall-issue laws increase crime. However, the only way that they can produce the result that shall-issue laws increase crime is to confine the span of analysis to five years. We show, using their own estimates, that if they had extended their analysis by one more year, they would have concluded that these laws reduce crime. Since most states with shallissue laws have had these laws on the books for more than five years, and the law will presumably remain on the books for some time, the only relevant analysis extends beyond five years. We extend their analysis by adding three more years of data, control for the effects of crack cocaine, control for dynamic effects, and correct the standard errors for clustering. We find that there is an initial increase in crime due to passage of the shall-issue law that is dwarfed over time by the decrease in crime associated with the post-law trend. These results are very similar to those of Ayres and Donohue, properly interpreted. The modified Ayres and Donohue model finds that shall-issue laws significantly reduce murder and burglary across all the adopting states. These laws appear to significantly increase assault, and have no net effect on rape, robbery, larceny, or auto theft. However, in the long run only the trend coefficients matter.
We estimate a net benefit of $450 million per year as a result of the passage of these laws.
We also estimate that, up through 2000, there was a cumulative overall net benefit of these laws of $28 billion since their passage.
We think that there is credible statistical evidence that these laws lower the costs of crime. But at the very least, the present study should neutralize any “more guns, more crime” thinking based on Ayres and Donohue’s work in the Stanford Law Review. We acknowledge that, especially in light of the methodological issues of the literature in general, the magnitudes derived from our analysis of crime statistics and the supposed costs of crime might be dwarfed by other considerations in judging the policy issue. Some might contend that allowing individuals to carry a concealed weapon is a moral or cultural bad. Others might contend that greater liberty is a moral or cultural good. All we are confident in saying is that the evidence, such as it is, seems to support the hypothesis that the shall-issue law is generally beneficial with respect to its overall long run effect on crime.
No...it doesn't.....it tries to link concealed carry to mass public shootings and I showed you how even the simplest question debunks the entire study on that point........
The study you found claims concealed carry gun permit numbers increase mass public shootings....I showed you that this is stupid and dumb as a claim...
You can't explain the link either...
Mass public shooters don't need a concealed carry permit to carry the gun to the place where they plan on committing mass murder.......
Criminals who can't legally buy, own or carry guns, can't get a legal carry permit to carry their already illegal gun.......and they are the ones committing almost all of the murder in this country in democrat party controlled cities...
Your study is crap.......
It can't prove that since making a connection between law abiding permit holders makes no sense...since the majority of all crime and gun murder is committed by people who can't legally have a gun permit for their already illegal guns.........
And I just posted other real studies showing that concealed carry, in fact, helps to reduce the crime rate......